
Subscribe to continue reading
Subscribe to get access to the rest of this post and other subscriber-only content.

Subscribe to get access to the rest of this post and other subscriber-only content.
Published On 12 December, 2023 – Source: From News Agencies
President Xi Jinping’s first state visit to Vietnam in six years seeks to deepen ties between the communist neighbors. Xi’s last visit to Vietnam in 2017 was for an Asia-Pacific economic summit in the coastal city of Danang.
China’s President Xi Jinping is in Vietnam seeking to strengthen ties between the communist neighbors as Hanoi deepens diplomatic relations with Western countries. The visit on Tuesday comes three months after United States President Joe Biden traveled to Vietnam as the major powers vie for influence in the Southeast Asian nation.
Xi was scheduled to meet Communist Party General Secretary Nguyen Phu Trong, President Vo Van Thuong and Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh, Vietnam’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs said.
Speaking after he arrived at Hanoi airport, Xi said he would talk with Vietnamese leaders on “the overall, strategic, and directional issues of China-Vietnam relations, as well as international and regional issues of common concern, to push bilateral relations into a new stage”, according to Chinese state media.
Later in the day, the sides signed 37 agreements, including on cross-border rail development and trade. The two countries have also agreed to conduct joint patrols in the Tonkin Gulf, according to reporters who witnessed the signing ceremony.
Vietnam has long pursued a “bamboo diplomacy” approach, striving to stay on good terms with both powers. It shares US concerns about Beijing’s increasing assertiveness in the contested South China Sea, but it also has political commonality and close economic ties with China.
Vietnam and China already share a “comprehensive strategic partnership”, Vietnam’s highest diplomatic status. Hanoi and Washington upgraded their relationship to the same level in September.
Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs spokesperson Wang Wenbin said Xi’s visit would involve discussions on “bringing China-Vietnam relations to a higher position”.
The agenda for the trip includes “politics, security, practical cooperation, the formation of public opinion, multilateral issues, and maritime issues”, he said.
Despite close economic ties, the neighbors have been at odds over boundaries in the South China Sea.
China has, over the past decade, expanded land reclamation in the South China Sea, creating militarised islands with runways, ports, and radar systems. Vietnam, along with Malaysia, Brunei, the Philippines, and Taiwan, also has overlapping claims in the territory.
During Biden’s September visit, Vietnam and the US jointly warned against the “threat or use of force” in the South China Sea.
In an opinion piece published in Vietnam’s Nhan Dan newspaper before the visit on Tuesday, Xi wrote: “Asia’s future is in the hands of no one but Asians.”
A “community with a shared future” between the two countries would have strategic significance, he added, while warning against rising “hegemonism” in the world, an apparent reference to the US, though he did not name it.
In September, Biden asserted that stronger ties with Vietnam were not about countering China, though US diplomacy across Asia and the Pacific has been focused on improving defense ties with countries to do just that.
China has been Vietnam’s largest trading partner for several years, with a bilateral trade turnover of $175.6bn in 2022. Imports from China, including crucial inputs for Vietnam’s manufacturing sector, make up 67 percent, according to Vietnam customs data cited by Vietnamese state media.
China has more than $26bn invested in Vietnam, with some 4,000 active projects.

Biden’s Vietnam embrace repeats past US mistakes | Politics | Al Jazeera
The US is again attempting to draw Vietnam into superpower politics. But much of the world is wary of Washington’s game.


To complete my review of this External Debt of Africa and all the cascade of difficulties inherited from such exposure, in this present article and in addition to its inherent analysis, I have included a selection of precedent and relevant articles I wrote on the African Debt and Natural Resources.
This approach of having other sustaining articles will allow a broader view of the imbrications and the cause-effect relationships existing between the increase of the external debt and the reduction of earnings for the African states pushing their budgets to be financed by new debts instead of revenues from their resources. In other words, my objective is to explain when, how, and where the responsibilities of these International Financial Institutions have for decades fueled by their programs and their conditionalities, including recommendations that fueled riots such as the reduction of public subsidies for basic food needs of the population while parading their willingness to open the hose to flood financially weakened African financial chancelleries with loans, They acted like pyro-loans and like Fire Fighters mentors while knowing that all their programs for decades already will bring another crisis that will impose to the African borrowers to halt their infrastructural projects and their social leverage of the most vulnerable classes of their populations.
It seems that these international financial institutions including the IMF refused to learn from all these missed managed financial African years and continued to leverage Africa with debt instead of making Africa the recipient of Foreign Direct Investments that could transform and process the natural resources and transferred technology to form new generations of unemployed youths.
The external debt of Africa is one of the brakes that is stopping regional integration and slowing continental market construction. It is a leverage as it has been the case since the discovery that Africa has strategic mineral resources. These natural resources became first the reason for Africa to be at this level of indebtedness. One of the leaders of African Independence said that the natural resources of Africa are a Curse and he was not that far from the Truth given that it has corrupted all the ruling system of the newly independent African countries and have embedded strifes, wars and disputes as well as coup d’etat as expression of civil wars.
“Conflict over natural resources has made Africa the focus of international attention, particularly during the last decade. From oil in Nigeria and diamonds in the Democratic Republic of Congo, to land in Zimbabwe and water in the Horn of Africa, the politics surrounding ownership, management, and control of natural resources has disrupted communities and increased external intervention in these countries. Such conflict has the potential to impact natural resource supply globally, with both local and wide-reaching consequences. The United States, for example, estimates that a quarter of its oil supply will come from Africa by 2015.” – https://muse.jhu.edu/pub/316/monograph/book/85497
For all these reasons, we will also emphasize the reasons for the setback experienced by the restructuring and rescheduling of Zambia’s External Debt and how even in the long run other projects such as the Liboto Corridor Project have played the role of the double edge sword with 2 sharp sides the long run can be transformed also in the Sword of Damocles that will be put on the top of the Zambia Head.
African School of Development and Financing should use the case of Zambia to teach our rulers and leaders how to avoid being attracted, lured, and finally punished by those from the start who sought and wanted to control and make the Zambian economy obey their principles and concepts of Neo-liberal development imported from outside while they will end by exporting to themselves and their benefit all the internal mining goodies and local values.
Read more in the article:

Zambia is a Typical Study and an Open TextBook on how to fall into the modernization net and at the same time how to avoid falling into the External Debt Trap framed and camouflaged inside a Neo-liberal strategy of infrastructural upgrade through adopting the financing tools from and furnished by Westernized State-controlled development policies and their army of corporate officers leading up Zambia being transformed into a bargaining chip in the international competition between the West and the East.
The French expression “tirer les marrons du feu” literally means “to pull the chestnuts out of the fire”. It can also mean:
To do the dirty work
Or to reap the benefits of something
If we can emphasize and identify who is/are benefiting from these financial, economic, social, and institutional unstable and disturbing trends in Africa we will have the reasons for this debt madness and the cascade of financial difficulties plaguing simultaneously so many African countries – The Club of African Mad Dog Debt versus the Club of Paris and International Finance Predators.
European companies in the 1800s, Europeans extracted natural resources from Africa to fuel their trade and industry. They stole resources like rubber, ivory, copper, cattle, diamonds, and coffee. The so-called subcapitalist and neocolonialist approaches are still in play in some regions that were invested by Europeans in the early times.
Around this extractive method was built a temporary structure of exploitation worse than the ones built by the Gold diggers knowing that the depletion was near so no investments were made in the surrounding infrastructure or in the logistics of the value transfer and the transformative units. Villages made of shacks dominated the horizon and the only stone building was the ones of the company office. These European companies were not willing to upgrade or renovate their means of exploitation or they could no longer exploit with the same methods given the other countries willing to change such means and shortsighted strategy of mining giving the isolation of the mines and their geographical location far from all supervision by the central authorities.
Tragedy of Endowment and Natural Resource Curse in Africa
Some examples of natural resource conflicts in Africa include:
Civil wars
Water scarcity
In fact, the region where a natural resource exists and is exploited from oil to stones, this region is where all the spoliation of lands, the deprivation, the corruption and the pollution, and abuses of tribal rights, injustices, inequities in resource distribution along with standards of poverty and lack of good governance are all present and are the dominant factors of deny and conditions of existence for the majority of the local population.
These conditions have already given the creation of the wise appellation and reputation that is: When an African owns a Mining Business, it is Malediction for the entire country.” From oil in Nigeria and diamonds in the Democratic Republic of Congo, to land in Zimbabwe and water in the Horn of Africa, the politics surrounding ownership, management, and control of natural resources has disrupted communities and increased external intervention in these countries. The rudimentary extraction, processing, and use of natural resources are causing environmental problems such as air, land, and water pollution; disruption or destruction of ecosystems; and a decrease in biodiversity while promoting theft, detournement, and pillage that also impact the living conditions of the local population justifying repression and neglect by local and central authorities.
With such an important presence of China in Africa, a dramatic change took place that was also imposed by the consequences and the riddles going through the energy international market as a result of the Russia – Ukraine war and the advantages that gave to the oil producers and distributors to take advantage of such crisis by imposing their own conditions and levels of pricing for energy products. The world market followed a trend of inflationary burst that made the members of the European Union rethink their sanctions against Russia and their complete obedience to the financial directives coming from Washington while the U.S. oil corporations played the game with their own goals and purposes.
The European Union needed to find other alternatives to supply its members with the needed fuels of energy, and Africa was then solicited as the new partner in this new distribution of power and energy around the world. Coming to Africa by the back door, having a reputation for being part of the colonial and neo-colonial relationships, members of the European Union had and still have a hard time conveying and convincing African people that they are new minds and are bringing new means and approaches to build new bilateral relations and connections.
China is the largest single-country trading partner with sub-Saharan Africa. They buy one-fifth of the region’s exports, including metals, minerals, and fuel. China also provides most of the manufactured goods and machinery imported by African countries. The African Clusters for the Trade and Investment Rivalries Between the Western Economies and China
Despite all these involvements and investments, African countries remain exposed to the risk of defaulting on their external obligations. Africa faces many economic challenges, including:
Other challenges include:
Some ways to improve Africa’s economy include:
The IMF has provided over $50 billion to the region between 2020 and 2022. As of March 2023, the IMF had lending arrangements with 21 countries. In recent study on Africa, the International Monetary Fund emphasized that correction and adjustment of the State Fiscal Policy can provide solutions for the financial difficulties and the external debt distress in Africa.
Here is an extract of the study conducted and published by the IMF on this thorny question of external public debt in Africa:
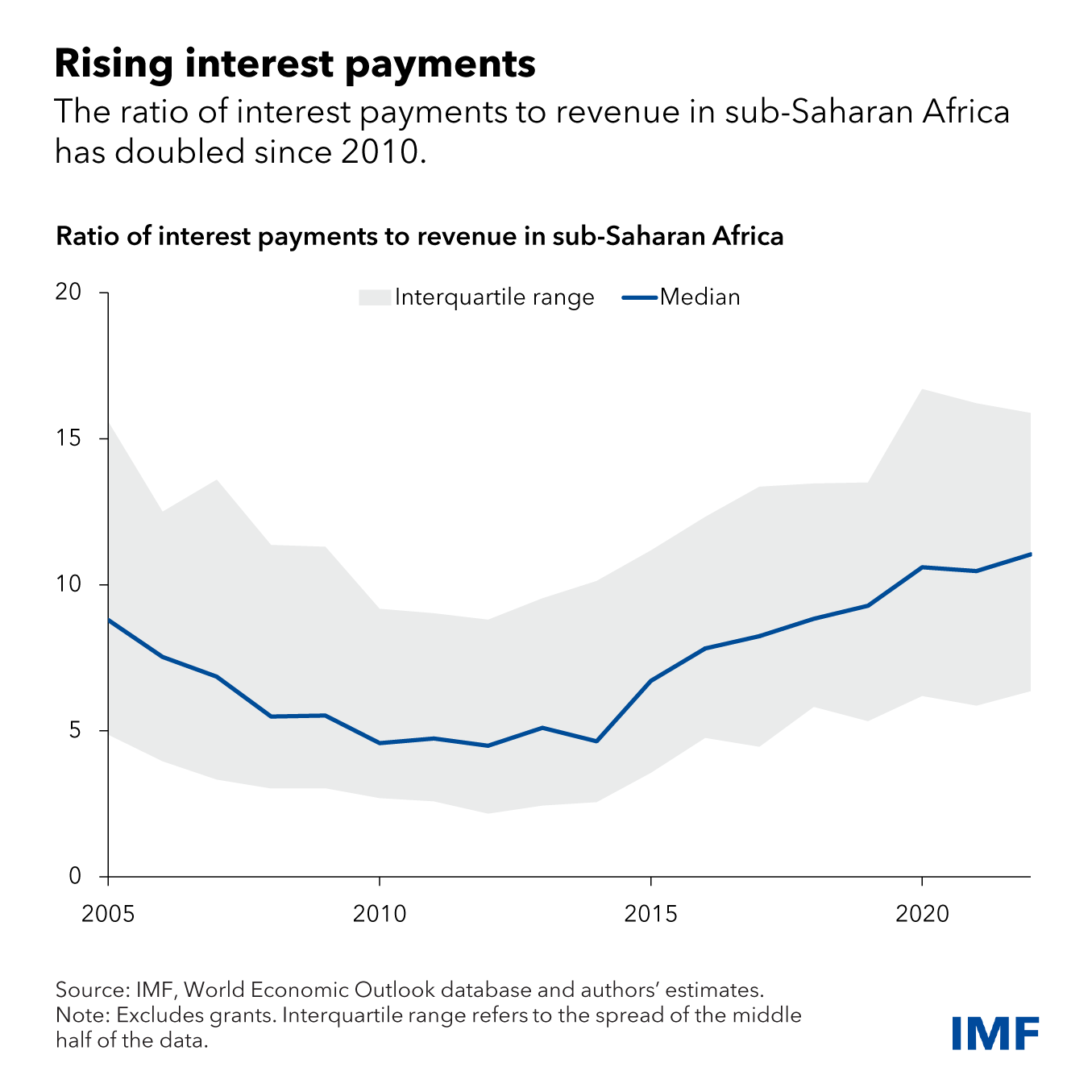
Public debt in the region has risen to levels not seen in decades
The average debt ratio in sub-Saharan Africa has almost doubled in just a decade—from 30 percent of GDP at the end of 2013 to almost 60 percent of GDP by end-2022. Repaying this debt has also become much costlier.
The region’s ratio of interest payments to revenue, a key metric to assess debt servicing capacity and predict the risk of a fiscal crisis, has more than doubled since the early 2010s and is now close to four times the ratio in advanced economies. As of 2022, more than half of the low-income countries in sub-Saharan Africa were assessed by the IMF to be at high risk or already in debt distress.
These trends have sparked concerns of a looming debt crisis in the region. A recent IMF paper offers possible solutions to prevent this from happening. It identifies five policy actions African governments can take to preserve the sustainability of public finances, while also achieving the region’s development goals.
1. Set a course: re-anchor fiscal policy through a credible medium-term strategy
In most sub-Saharan African countries, fiscal policy focuses excessively on short-term goals and is not guided by a clear medium-term strategy. This lack of anchoring has resulted in frequent breaches of fiscal rules and ever-increasing public debt levels.
A more strategic approach to fiscal policy would be preferable by setting explicit debt targets that integrate key policy trade-offs between debt sustainability and development objectives, rather than focusing narrowly on short-term fiscal deficits. The paper suggests a novel approach to estimating country-specific medium-term debt anchors, which ensures that debt service costs remain manageable. According to this methodology, the median debt anchor for the region is about 55 percent of GDP; slightly more than half of the countries were above their anchor at end-2022.
2. Get ready: undertake fiscal adjustment to bring debt back to a safer level … Read more at:


By Fabio Comelli, Antonio David, Luc Eyraud, Peter Kovacs, Jimena Montoya, and Arthur Sode: September 26, 2023, Public debt in the region has risen to levels not seen in decades. … Continue Reading

Approved in August 2021, the three-year program (2021-2024) of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) with Gabon, supported by the Extended Credit Mechanism (EMDC), faces some difficulties. Already the first and second review of this program concluded in 2021 allowed the IMF to disburse 155.29 million US dollars (approximately 96 billion FCFA) for Gabon within the framework of this program.
Indeed, the budgetary support that Gabon had hoped for since the end of December 2022 as part of the third review of the said program has still not been validated by the financial institution. And for good reason, the “third review of Gabon’s program is on hold due to recurring external debt arrears, budgetary slippages and slow progress on structural reforms ,” the IMF said in a recent report on common policies. in support of the reform programs of member countries, notably Cemac.
At the end of a mission carried out in November 2022 by the IMF services in Libreville with a view to collecting the information necessary to validate or not new budgetary support for Gabon within the framework of the MEDC, the resident representative of the IMF Agou Gomez He was rather reassuring, affirming that several progress had been made by Gabon.
Even if efforts are being made by local authorities in the management of public finances, several challenges remain. According to data from the General Debt Directorate, Gabon’s public debt stock in 2022 stood at 7,131.7 billion FCFA. A portfolio dominated at 63.4% by external debt. And during the first 9 months of the year 2023 according to data from the Ministry of the Economy, this public debt was paid off to the tune of 1010.8 billion FCFA. However, there are still arrears to be cleared.
The IMF lowers its growth forecasts for Gabon in 2023
The IMF recommends that Gabon strengthen its fiscal pressure in the face of funding shortages
Regarding structural reforms, the IMF had, for example, required the Gabonese authorities to ensure that the 2023 budget should “make it possible to find the balance between the preservation of social peace through subsidies, but also the preservation or savings from the oil surplus that Gabon reaps ,” said the resident representative of the IMF in Gabon Agou Gomez in November 2022.
If the program with Gabon is currently on hold, that of the other countries-members of the Economic and Monetary Community of Central Africa (Cemac) has undergone some developments. For example, program reviews for Congo and Cameroon were completed, and a new three-year Extended Credit Facility (ECF) agreement was recently approved for the Central African Republic. Discussions continue on a possible agreement between the IMF and Equatorial Guinea during this second half of 2023.
Source: Extracts by Sandrine Gainne – (Le Nouveau Gabon)
According to the World Bank, the Arab world made important progress to eliminating extreme poverty, boosting shared prosperity, increasing school enrollment, and reducing hunger, child and maternal mortality.
The subsidy model is both expensive and inefficient, nurturing corruption and waste. Nevertheless, it is simple to administer and enjoys a high rate of public approval.
In Egypt, the International Monetary Fund demanded subsidy cuts following the negotiations with Sadat’s government in 1976 – which sparked the 1977 bread riots.
What went wrong? In two words, food prices.
In North Africa, the squeezing of tight belt policy to pay the interest was to end the subsidies to the price of bread which was the sparkle to the Arab Spring. Middle East and North Africa depend more on imported food than anywhere else. Most Arab countries buy half of what they eat from abroad and between 2007 and 2010, cereal imports to the region rose 13%, to 66m tonnes. Because they import so much, Arab countries suck in food inflation when world prices rise. In 2007-08, they spiked, with some staple crops doubling in price. In Egypt local food prices rose 37% in 2008-10.
During the years leading up to 2011, the world witnessed a sharp rise in agricultural commodity and food prices. Increased demand from emerging economies such as China and India combined with climate-change induced harvest losses. The FAO cereals price index soared to 241 in 2011, up from 119 in 2006 [3].
Most Arab governments responded by reducing import tariffs and increasing subsidies and public sector salaries. These “corrective” actions, far from seeding calm, fed dissatisfaction. The anger came from a surprising place. The Arab poor already spent two thirds or more of their income on food [4] remained sullen. It the urban middle-class responded with fury.
Consider Tunisia. In 2010, Zine El Abidine Ben Ali’s regime faced a crisis. Although overall unemployment stood at 13% in May 2010, it reached 26,7% among local youth aged 15 to 29 and more than 50% in some inland areas. Well educated young people found no opportunities.
Free market reforms supported by the International Monetary Fund aggravated the misery. Subsidies to small scale farmers were slashed. The goal was instead to grow manufacturing exports and increase tourism. Rural inland Tunisia suffered, while the productive coast prospered.
On farms, the emphasis became growing vegetables and fruits for export. The country moved away from traditional rain-fed to irrigated agriculture. Given the importance of grain in the local diet (around 50% of food energy comes from cereals in Tunisia), imports soared: they were equal to 64% of consumed cereals between 2006 and 2008).
According to the Office for North Africa of the Economic Commission for Africa (UN) in 2012. Tunisia’s agriculture trade balance deficit increased from $125.5 million in 2005 to $873.3 million in 2010. Prices of food rose 6.8% in 2010, compared to a mere 0.1% in 2005. The ratio of food subsidies to GDP doubled.

BREAD, FREEDOM, AND MIGRATION: THE ROLE OF FOOD IN THE ARAB AWAKENING
Alessandro Balduzzi: 22 May, 2019, Bread, Freedom and Migration: the Role of Food in the Arab Awakening, Barilla Center for Food and Nutrition. North Africa’s short-lived Arab Spring of 2010-11 illustrates a disastrous cycle of conflict, food insecurity, and forced … Read more
That was the Simple Past mixed to the Imperfect Present on how to balance the State Budget and today the IMF is again recommending to end the public subsidies and this time for the pricing of oil.
MARRAKECH, Morocco, Oct 16 (Reuters) – The International Monetary Fund (IMF) urged sub-Saharan African policymakers last week to cut costly fuel subsidies and raise more in taxes, measures that may be hard to implement as governments grapple with tough spending choices amid high debt.
The region has been hit by repeated economic shocks since 2020, from the COVID-19 pandemic to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and rising U.S. interest rates, putting cash-strapped, debt-laden governments in a political and fiscal bind.
However, the IMF’s prescriptions, set out at its annual meetings last week, are often painful to administer. Countries from Ghana, which defaulted on its debts last year, to Kenya, which must pay back or refinance a $2 billion international bond before next June, have seen violent protests against tax hikes and subsidy removals.
Meanwhile, the region’s debt-to-GDP ratio, which has already doubled to 60% in the last decade, could rise 10 percentage points in the next five years if its fiscal trajectory doesn’t change, according to a recent International Monetary Fund (IMF) report.
Earlier this month of October 2023, Kenya’s cabinet ordered government departments and ministries to cut 10% from their operational budgets for the fiscal year ending in June 2024.
Oil-dependent Angola, where crude production has been lower than expected, is going through “extreme austerity”, finance minister Vera Daves de Sousa told Reuters. The country froze some non-social spending two months ago, such as capital expenditure on projects that are less than 80% complete, she said. “We have to freeze up some expenditure just to make sure that we manage to continue servicing the debt and paying salaries and making sure that the country is functioning.”
Sub-Saharan Africa’s ratio of debt interest payments to government revenues of about 10.5% has more than doubled in the last decade and is about three times that of developed countries, according to the IMF. In many countries that ratio is much higher. Ratings agency Fitch forecasts it will reach 40% in Nigeria and 28% in Kenya, for example, next year.
High interest rates make refinancing debt prohibitively expensive for most African countries and have weakened their currencies against the U.S. dollar. Public spending could drop in real terms for the next five years in 26 Sub-Saharan African countries, according to forecasts by Oxfam International, an anti-poverty NGO.
“If you educate the people, you’re also going to increase productivity, you’re also going to increase human capital,” said Anthony Kamande, Oxfam’s inequality research coordinator. “But how are they going to do that if they do not have money, if the little that they have they are just spending on debt servicing?”
Some governments are taking the advice doled out by the IMF to cut fossil fuel subsidies that the fund says benefit wealthier people.
Senegal, Angola and Nigeria are among the African countries that have started to remove the costly but popular benefit.
In Angola, their partial removal earlier this year sparked deadly protests and its finance minister said it was considering slowing plans to axe the rest of the subsidies by 2025.
The IMF has warned that if Angola does not do so, then it will have much lower financial buffers to weather more economic shocks, such as oil prices falling.
“For us, the most important thing was to accept that we have a problem,” Zambia’s finance minister Situmbeko Musokotwane told reporters in Marrakech last week, referring to the country’s decision to restructure its debts after defaulting in 2020 and to implement economic reforms.
“To be able to pay for every child in school, we had to end subsidies on fuel because we could not do both,” he said. “We had to make those hard choices.”
Reporting by Rachel Savage, Editing by Emelia Sithole-Matarise
Africa Destiny: Zambia’s Bad Credit Bet for China and West Good Mining Gamble – Said El Mansour Cherkaoui Ph.D. … Continue reading

Africa Destiny and New World Game
Said El Mansour Cherkaoui November 21, 2023 – What we are witnessing actually has no precedent in the history of Africa. African Leaders are becoming the best guests to invite in this world … Continue reading
My work is analytical and investigative emphasizing the reasons and the impact of external debt which I have conducted for many decades with a focus on the development of African societies.
In France, while I was still a student at Sciences Po in Grenoble, I formulated a project on the Development of China and I presented it as the model to be imitated and followed by all these former African colonies which were during the 1970s, shaken by the brutality and sudden oscillations of the international market and the weight of foreign debt.
In 1977, I defended China as the Model of Development for Former Colonized Countries and I was put down the precipice and almost kick-out of the Sciences Politiques of Grenoble and I had to fight hard to continue my studies against as we say in French “contre vents et marées de mesquinerie et de sabotage ainsi que d’attaques racistes” to bring my lost ship to the port of knowledge and know-how.
My research like all the other previous ones was conducted through a projection and a prediction of the effects and manifestations that could be generated down the road and in the future of the countries or sectors that were the topics of my research.
Read more in the following 2 publications:
Chinese Development Model Defended: SciencesPo Grenoble Prize for Said El Mansour Cherkaoui
Said El Mansour Cherkaoui Ph.D. April 20, 2023 Introduction: France for me is above all and that during my fifteen years and more … Continue reading
Prize for Defending Africa Development with Chinese Model at SciencesPo – Grenoble – France

Said El Mansour Cherkaoui Ph.D. April 10, 2023 – China Ink Wrote an Attaching Memory in My Mind, 1977 – Africa Afrique Murée at … Continue reading
Provide consulting services to small, and mid-sized firms, minority and women-owned companies/cooperatives, and Entrepreneurs Tri Consulting Kyoto – TRI Solutions with Excellence and Innovation – TRI CK – USA YOU ARE PREPARING YOUR FUTURE EXPORT ACTIVITY TRI CK USA will help you select your target countries TRI CK USA will define and conduct a diagnosis to … Continue reading
Our Sponsors & Supporters
TRI CONSULTING KYOTO – TRI CK USA – saidcherkaoui@triconsultingkyoto.com – info@triconsultingkyoto.com
– TRI CK USA can help you to expand U.S. investment and business in Morocco and we can also help Moroccans to export to California and Californians to export to Morocco and Africa.
– TRI CK USA has known California for 35 years of residency, work, research, business operations, academic work, and building and expanding business from overseas, up to China.
– TRI CK USA facilitated the first import of Moroccan Products, Egyptian Products, Tunisian Products, and Cameroonian Products to California while opening up foreign markets for California.
saidcherkaoui@triconsultingkyoto.com
Said El Mansour Cherkaoui Ph.D. 11/26/23
Bibliographical Resources Consulted and Used in this Analysis:
Abiodun Alao: 2007, Natural Resources and Conflict in Africa: The Tragedy of Endowment. Book. Published by: University of Rochester Press
The first comprehensive account of the linkage between natural resources and political and social conflict in Africa.
Conflict over natural resources has made Africa the focus of international attention, particularly during the last decade. From oil in Nigeria and diamonds in the Democratic Republic of Congo, to land in Zimbabwe and water in the Horn of Africa, the politics surrounding ownership, management, and control of natural resources has disrupted communities and increased external intervention in these countries. Such conflict has the potential to impact natural resource supply globally, with both local and wide-reaching consequences. The United States, for example, estimates that a quarter of its oil supply will come from Africa by 2015 – https://muse.jhu.edu/pub/316/monograph/book/85497

African governments owe three times more debt to Western banks, asset managers, and oil traders than to China, and are charged double the interest, according to research released today by Debt Justice. Western leaders through the G7 have attributed the failure to make progress on debt restructuring to China, [1] but the data shows that this is mistaken. Just 12% of African governments’ external debt is owed to Chinese lenders compared to 35% owed to Western private lenders, according to the calculations based on World Bank data.
Africa’s consumer boom has been financed mostly by income generated from the export of natural resources. However, many of the region’s economies are based on commodity exports, making them beholden to the ups and downs of global commodity prices.
We have included and developed such an approach in the form of a wide selection of our publications, analyses, and reports on Foreign Direct Investment in the Subsaharan African countries, and through the example of Zambia. We have also analyzed the strategy pursued by the alliance of Western-based investors and their respective States in the European Union, the United States, and the International Banks. Their main concern is to limit and contain the presence of China in Africa.
Therefore, they devised a strategy to work together to reschedule the external debt of Zambia while advancing their pions in the mining industry within the regions surrounding and peripheral to Zambia such as the Lobito Corridor Project.
More details in each article are presented and listed below.
AFRICA TODAY in the VACUUM of LOCAL INVESTMENTS, ALIENATION of its OWN NATURAL RESOURCES, and DEPRIVATION of its HUMAN CAPITAL
by Said El Mansour Cherkaoui Ph.D.
In this article, we are offering you a mosaic of analyses that have pieces presenting each aspect of how this combination of opportunities and turf fighting is taking place around the mining sector in Central and Southern Africa. Africa has a number of challenges, including:
Natural resources
Africa is home to 30% of the world’s mineral reserves, 40% of the world’s gold, and the largest cobalt, diamonds, platinum, and uranium reserves. However, Africa is still one of the world’s poorest continents.
Human resources
Africa has a young and dynamic workforce, with more than 12 million young Africans entering the labor market annually. However, only 30% of them are able to find a job.
In 2010, the International Monetary Fund believes growth in sub-Saharan Africa will be 1 percentage point above the global average, and puts eight African countries in its top 20 fastest-expanding economies. Oil-rich Angola and Congo Republic will lead the charge with growth rates of more than 9 and 12 percent respectively, both beating China, according to the IMF’s most recent projections.
Dollar crisis
Africa is facing a dollar crisis, which is hindering the flow of foreign investment into its companies.
Access to energy
In 2022, 600 million people in Africa, or 43% of the continent, lacked access to electricity.
In 15 resource-intensive sub-Saharan African countries, mining contributes about 10% to GDP. In most of these countries, mining exports represent 50% of total exports, so many of the mineral-rich economies of Africa risk continuing to be dependent on mining. Mining has also led to the development of urban centers, such as Tororo, Kasese, Mombasa, and Kakamega.
In South Africa, mining accounts for up to 60% of exports. The country’s mining sector contributes about 8% to the gross domestic product.
Africa has a large amount of mineral reserves, including:
Some of the major mining countries in Africa include the Democratic Republic of Congo, South Africa, Namibia, Zimbabwe, Botswana, Congo-Brazzaville, Gabon, Guinea, and Sierra Leone.
In 2022, Africa accounted for less than 10% of global mining exploration spending and less than 5% of the sector’s global revenue. However, the need to secure new sources amid sanctions on Russia has increased the risk appetite for major miners.
Already in 2021, investment flows to Africa reached a record $83 billion. European investors remain the most important source of FDI stock in Africa, but the relative share of Africa’s FDI stock originating from Europe declined over the past decade, while Asia’s share increased.
The study also covers U.S. FDI in Africa.
European investors are the largest holders of foreign assets in Africa. The United Kingdom ($65 billion) and France ($60 billion) are the largest holders.
The United States is the largest investor in Africa by project numbers. However, in terms of capital, the US trails the UAE, France, and India.
China is the world’s largest investor in Africa in terms of total capital. Between 2014 and 2018, China invested more than $72 billion in Africa.
European countries are the largest holders of foreign assets in Africa. The United Kingdom and France are the largest holders, with $65 billion and $60 billion respectively.
Other major investors in Africa include:
United States, Japan, China, Australia, Netherlands, Belgium, Germany, Luxembourg.
Some of the sectors that receive the most investment in South Africa include Financial, Mining, Manufacturing, Transportation, and Retail.
This is not professional financial advice. Consulting a financial advisor about your particular circumstances is best so contact us
Contact the Author for public speaking, advising, or consulting engagement, please send an email to: saidcherkaoui@triconsultingkyoto.com
Some of the top African countries with the largest foreign investments include:
Here’s some information about FDI in Africa by country:
According to UNCTAD, European investors are the largest holders of foreign assets in Africa. The top three countries are:
Other countries with large foreign investments in Africa include:
In 2021, South Africa was the main recipient of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in Africa
China is the world’s largest investor in Africa in terms of total capital. Between 2014 and 2018, 16% of FDI into Africa came from China. The United States and France held 8% of the total FDI. From 2016–2020, China invested more than $71 billion in greenfield FDI in Africa. China is the largest investor in Africa in terms of total capital. Between 2014 and 2018, China invested more than $72 billion in Africa, creating over 137,000 jobs. Nigeria is one of China’s largest investment partners in Africa.
United States – In 2022, the United States invested $46.17 billion in Africa. The United States is the largest investor in Africa by project numbers. In 2023, the US contributed 13% of Africa’s total investment. The US has invested $46.17 billion in Africa in 2022. This is a rise from 2020 when the US invested $44.81 billion. The US has also helped close over 800 trade and investment deals with 47 African countries, worth over $18 billion. The US private sector has also closed deals worth $8.6 billion. The US has also provided humanitarian assistance to Africa. In 2022, USAID provided over $6 billion in humanitarian assistance. In the past decade, the US has generally allocated around $8 billion annually to Africa.
The US has also invested in South Africa. In 2022, the US invested $7.4 billion in South Africa, which was an 11.9% increase from 2021. This was an increase of 11.9% from 2021. The US has invested in manufacturing, finance, insurance, and mining in South Africa.
European investors are the largest holders of foreign assets in Africa. The United Kingdom, France, and the Netherlands are the largest holders of FDI stock in Africa. The EU is Africa’s largest trading partner, followed by China.
United Kingdom – In South Africa, the United Kingdom accounts for three-quarters of the total FDI.
France – France holds 8% of the total FDI in Africa.
African Countries Recipients of Foreign Direct Investments
Egypt – In 2021, Egypt received $5.1 billion in FDI.
Nigeria – In 2021, Nigeria received $4.8 billion in FDI.
Zambia – After two years of negative FDI, Zambia received $116 million in 2022.
Mining Indaba is Africa’s premier mining event and one of the largest mining events in the world. Some of the largest mining companies in Africa include BHP Billiton, Rio Tinto, Anglo-American, Xstrata, and Barrick.
To contact the Author for public speaking, advising, or consulting engagement, please send an email to: saidcherkaoui@triconsultingkyoto.com
Rooted in history, the BRI carries forward the Silk Road spirit At around 140 … Continue reading China Global Strategy

Belt and Road Initiative: A Key Pillar of the Global Community of Shared Future … Continue reading
To contact the Author for public speaking, advising, or consulting engagement, please send an email to: saidcherkaoui@triconsultingkyoto.com

You Need to Know more about TRI CK USA
You Want to Introduce Yourself and your Business or Project
Please complete and Submit this form


Africa Destiny: Zambia’s Bad Credit Bet for China and West Good Mining Gamble
Contact author – saidcherkaoui@triconsultingkyoto.com – When the Missionaries arrived, the Africans had the Land and … Continue reading
Africa: New Mining Turf for West – Far East International Competition
This is the time for African Rulers and decision-makers to have a better place at the table of the distribution of international investment mapping and localization around the world.
Africa has the opportunity not to rely just on foreign aid by presenting an image where investment is made for small projects by small businesses, women-owned businesses, and locally and regionally enclaved initiatives that are more for subsistence and self-sufficiency. These projects are too small to reach the level of defining national policy or to contribute to the overall development of regional localities or national levels.
As luck would have it, Germany on one side and the European Union on the other with the USA, Lobito while Zambia had just hit a slump in terms of paying its international debts. Investment does not wait, it is better to strike the iron while it is red, and hot in front… Hot is coming watch out and make way, and the train of capital is disembarking in the remote mines of the heart of Southern Africa to remove China from the landscape and from the African horizon which also aims to reduce the expansion of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Public-Private Partnership Opportunities
The Lobito Corridor Project offers unparalleled opportunities for U.S. businesses. With a commitment to sustainability and green innovation, the private sector can be part of the corridor’s transformative impact on Africa. Serving as a vital link for landlocked countries to access international markets, the Corridor project opens avenues for U.S. businesses to establish partnerships, diversify supply chains, and contribute to the economic development and diversification of the region.
The U.S.-Africa Business Center (USAfBC) and our American Chambers of Commerce in partner nations are actively engaged in the development of the Corridor. On March 6 in Washington, DC, as part of the 2024 Powering Africa Summit, the USAfBC is organizing an executive ministerial roundtable on the Corridor featuring key stakeholders from the U.S. and African public and private sectors. This roundtable will focus on financing the energy transition to power the Lobito Corridor project and convene public and private sector leaders to explore sustainable energy solutions and financing opportunities for the corridor’s development.
Source: The Lobito Corridor: Building Africa’s Most Important Railway
Developing the Lobito Corridor is more than an infrastructure project. In partnership with the U.S. government, private sector engagement could unlock growth across three African countries and beyond.
China Belt and Road Initiative Linking Asia with Africa and Europe
The Belt and Road Initiative is a global infrastructure development strategy adopted by the Chinese government in 2013. The BRI aims to connect Asia with Africa and Europe via land and maritime networks.
Here are some related interesting articles and topics to read:
Rooted in history, the BRI carries forward the Silk Road spirit At around 140 … Continue reading China Global Strategy Built with BRIC and BRI
The goals of the BRI are to:
The BRI is also known as the “One Belt One
Road” (OBOR), the “Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st-century Maritime Silk Road” or just the “New Silk Road”. The BRI has invested in more than 150 countries and international organizations. The BRI investment projects are estimated to add over USD 1 trillion of outward funding for foreign infrastructure over the 10-year period from 2017. The BRI has also increased China’s influence in Africa by providing loans to participating countries to construct infrastructure in various sectors. The BRI has helped to fill infrastructure gaps and boost economic growth in participating countries. As of August 2023, 155 countries have signed up to the BRI. This includes 53 out of 54 African nations.
The projects in Africa focus on transport and power, including:
The BRI has the following positive effects:
The BRI and the initiative were translated by China into billions of dollars invested in the construction of roads, ports, railways, and other critical infrastructure. These projects are not only enhancing connectivity within the continent but also providing China with unprecedented access to Africa’s vast mineral wealth, particularly in countries like Zambia and the Democratic Republic of Congo (more than 80% of copper mines in the DRC for instance are already Chinese-owned), which boast abundant reserves of copper and other essential minerals. Overall, China has spent more than a trillion dollars on projects at least partly intended to secure the supply of resources key to the energy transition.
Here are some related interesting articles and topics to read:

Belt and Road Initiative: A Key Pillar of the Global Community of Shared Future … Continue reading

Direct intervention of the authorities of the United States and the European Union in shaping the landscape for investors and operating companies as the scouts and the explorers if not the preparatory of the deals to be concluded and guaranteed by the African governments to be allocated directly without any offer or bid as used to be the case for international projects and projects that African countries were seeking foreign investments for their materialization.
Therefore, the representatives of the U.S. and the European Commission are acting as prospectors, negotiators, and deal-makers on behalf of their national companies. This approach is also consolidated by the willingness of Western-based financial institutions to be part of this move by supporting projects where U.S. and European governments are setting the pace of negotiations and the process of facilitating their conclusion.
The United States and the European Union welcomed the recent commitment by Angola, Zambia, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to develop the Lobito Corridor. The Lobito Corridor has the potential to generate significant economic benefits for Zambians by upgrading critical infrastructure, expanding export possibilities, boosting the regional circulation of goods, and promoting job creation and regional travel.
The Authorities of Washington are directly involved in securing the environment and the countries that are going to be part of this project and delegations of U.S. Diplomats and Officials have been visiting the capitals of the neighboring African countries:
November 21, 2023: Readout of Director of National Intelligence Avril Haines’s Travel to the Democratic Republic of Congo and Rwanda
Director of National Intelligence (DNI) Avril Haines traveled to Rwanda and the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) on 19-20 November. The DNI was joined by Assistant Secretary of State for African Affairs Molly Phee and Special Assistant to the President and NSC Senior Director for African Affairs Judd Devermont.
DNI Haines met with Rwandan President Kagame and Congolese President Tshisekedi to secure commitments from both leaders to de-escalate tensions in eastern DRC. Acknowledging the long history of conflict in this region, Presidents Kagame and Tshisekedi plan to take specific steps to reduce current tensions by addressing the respective security concerns of both countries. The steps are drawn from previous arrangements reached with the support of neighbors under the Luanda and Nairobi processes.
The U.S. government welcomes, and intends to monitor, these DRC and Rwandan steps towards de-escalation, and plans to support diplomatic and intelligence engagements between both countries to foster greater security and prosperity for the Congolese and Rwandan peoples.
Acting Special Coordinator Matza’s trip follows a joint statement last month from the United States and the European Union on support for the development of the Lobito Corridor. Prior to that, at the G7 Summit in Japan in May 2023, President Biden announced a U.S. government investment of an initial $250 million (5 billion kwacha) to develop the Corridor.
The primary objective of Special Coordinator Matza’s visit to Zambia was to prepare for launching the feasibility study for the Zambia-Lobito railway and to explore developing projects across multiple sectors in Zambia.
LUSAKA – U.S. Acting Special Coordinator for the Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment, Helaina Matza , traveled to Zambia on October 19 and 20, 2023 to advance U.S., Zambian, and EU efforts to develop the Lobito Economic Corridor and the Zambia-Lobito Greenfield railway, which connects the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Zambia with global markets through Angola.
During her visit to Zambia, Acting Special Coordinator Matza and U.S. Ambassador to Zambia Michael Gonzales met with President Hakainde Hichilema, Minister of Finance Situmbeko Musokotwane, Minister of Energy Peter Chibwe Kapala, and other senior government officials to discuss how the United States and Zambia can best partner together to develop the Corridor. The delegation held multiple discussions with logistics, mining, agricultural, and energy companies to discuss how technical and financial resources can be leveraged to benefit the project and how the corridor can spur investment and job creation in these sectors. They also met with the European Union Ambassador to Zambia to strengthen U.S.-EU collaboration on the project.
Here are some related interesting articles and topics to read:
The Lobito Corridor is a multimodal transport facility in Africa. It consists of a network of roads, railway lines, airports, and the Port of Lobito. The project involves laying hundreds of miles of track from Zambia’s Copperbelt province to an existing line in Angola.
The Lobito Corridor is expected to:
The Lobito Corridor Project has three main components:
The Lobito Corridor has the potential to generate significant economic benefits for Zambians by upgrading critical infrastructure, expanding export possibilities, boosting the regional circulation of goods, and promoting job creation and regional travel.
As an immediate next step, the United States and the European Union will support the Governments in launching pre-feasibility studies for the construction of the new Zambia-Lobito railway line from eastern Angola through northern Zambia. This builds on the initial U.S.-led support to refurbish the railway section from the Lobito port in Angola to the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Here are some related interesting articles and topics to read:
“Once transport infrastructure connecting all three countries is fully operational, the Corridor will enhance export possibilities for Zambia, Angola, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, boost the regional circulation of goods, and promote the mobility of citizens. By significantly reducing the average transport time, the new railway will lower the logistics costs and carbon footprint of exporting metals, agricultural goods, and other products, as well as for future development of any mineral discoveries.
The United States and the European Union plan to explore cooperation in three specific areas:
Specifically, this includes developing clean energy projects to increase the power supply to surrounding communities, supporting diversified investment in critical minerals and clean energy supply chains, extending digital access, growing agriculture value chains to enhance local food production for the region’s expanding population and to address global food insecurity, as well as augmenting local workforce training, support for small and medium enterprises and economic diversification.” Click here to read more on this.
To contact the Author for public speaking, advising, or consulting engagement, please send an email to: saidcherkaoui@triconsultingkyoto.com

You Need to Know more about TRI CK USA
You Want to Introduce Yourself and your Business or Project
Please complete and Submit this form
Lobito Corridor: United States and European Union Direct Entrance in Mining Industry
China Business Panorama
Internet helps to save time with a high return on investment. Buying from a mobile and being delivered where you want is time and money-saving. Following a study, 75% of the Chinese population that browses on the internet, does it on a mobile phone. The other conclusion of the study is that there is an overlap between the population that uses the internet and social media and the consumers with purchasing power. With the most Internet users in the world, China has the world’s largest and fastest-growing social networks and e-commerce platforms.
According to PwC Economic Quarterly Q1 2017, the national online retail sales of goods and services in China reached 1.4 trillion Yuan in the first quarter, 32,1% higher than in Q1 2016. In comparison, retail sales of the physical stores went up by 7.2% only. In many countries where one does not have often a say, online consumers have a say on social networks and can chat with each other and share experiences.
Mohammed Khalil: December 10, 2017, What if the future of modern trade is already in China?
Giving feedback on products, services, and brands, and their validation through ratings is a form of power that consumers have. This gives trust, transparency, and security, that institutions cannot always offer. Health care requires trust, transparency, and security. A McKinsey survey in 2017 showed that 65 % of online shoppers in China are seeking ways to lead a healthier lifestyle.
Next to being the largest e-commerce market, China is also the most innovative e-commerce in the world. Innovations such as mobile digital payment ecosystems, and virtual reality are probably key reasons for the rise of e-retail spending. It seems that this offers availability and value to customers even in rural markets. Incorporating digital payments into existing services will open up new markets for micro, small, and medium enterprises and transform the way people transact around the world, including developing countries. Innovative business models are required for e-commerce in areas where mobile digital payment ecosystems are not yet possible.
China is today, overall, an intermediate country, far from extreme poverty. Its HDI (0.745) places it 94th in the world (out of 177 countries). Its PPP GDP stands at $4,580 per capita, with constant progress. Such figures, however, are only averages: for the rural population, they are very much lower. In some respects, China in the 2000s remains a poor country.
Over the past twenty years, however, China has been progressing very rapidly. It is even the country in the world with the strongest economic growth. The GDP thus grew by 8.2% per year between 1975 and 2002 and by 8.6% per year between 1990 and 2002, a multiplication of 2.5 in 12 years, by almost 8 in 27 years! No other country can boast of such economic development which has placed the republic on the path which today makes it the second power in the world.
Over the past two decades, China has become a manufacturing hub and the world’s largest exporter of goods, transforming from an emerging economy to an economic superpower.
According to the latest estimates of the economic outlook for IMF, the country will represent 18.8% of global GDP at purchasing power parity (PPP) this year. A figure up by more than 10 percentage points compared to the early 2000s, when the United States and the European Union were still far ahead in terms of economic production.
Over the past twenty years, the United States and major European economies have seen their superiority challenged by the emergence of new powers, such as China, India, and other countries. While the United States saw its share of global GDP decline from 19.8% to 15.8% between 2002 and 2022, that of the European Union fell from 19.9% to 14.8% over the same period (keeping in mind that the United Kingdom’s exit from the EU also contributed to this decline).
The gap between China, the United States, and the EU is likely to widen in the coming years, as the outlook is rather bleak for the latter two economies, which are at risk of entering a recession, while the Chinese economy should be able to continue to post single-digit growth rates (close to 5%).
China is working on establishing all these milestones and beyond.
Battling China is the reward given to China as recognition of its outstanding performances realized during just 5 presidents du Developpement Global de la Chine – 4 Leaders Pieds de la Table de Jeu Technologique de la Chine and 50 years of hard work and devotion to national development policies and goals.

Dr. Said El Mansour Cherkaoui
saidcherkaoui@triconsultingkyoto.com – https://triconsultingkyoto.com
China’s Rise to Economic Preeminence
As the world economy continues to grapple with supply chain issues (in part) caused by the “zero Covid” health policy and lockdowns in China. It has become sadly clear just how bad the global economy is vulnerable to regional disruptions, especially if they occur in China, the largest supplier of goods on the planet.
Yes, we are capable of it. Except that let’s not forget the progress of China, whose GDP per capita was almost similar to that of African countries in the 1960s. But mainland China, broken up during the occupations, had already achieved its unification and was continuing its cultural revolution.
In China, we better apply God’s commandments (treat your neighbor as yourself, don’t steal, don’t kill, hate corruption, etc.) but we talk less about God or Allah, even less about churches/ mosques than in Africa.
This means that the religion of development and community well-being was better instilled in the population thanks to education controlled by nationalists and above all dedicated leaders.
Africa, for its part, finds it difficult to escape from religious or even community quarrels, which gives rise to Western and Eastern sects. Our societies face serious mentality problems and our true leaders struggle to play their role or are simply pushed aside.
However, unity of visions is a prerequisite for unity of actions and an important factor of Power, whether political or economic.
Response from Said El Mansour Cherkaoui
To the Attn. of: Meying Mengue & Adamou BOUBACAR
Religion is not the cause, it is used as a reason for anger and revolt against the aspirations of the people to live peacefully.
None of the 3 divine religions dictate that you live in misery and go kill others to steal from them.
China developed because it had leaders who went to see up close what Capitalism is in its essence by working and closely studying the capitalist system in its relations of production and distribution of the most -value and its relations with the USSR and China to ensure the growth of this added value
Even the Leader of Vietnam did the same. Nehru of India also followed this trajectory to understand what British capitalism is. We can continue the examples with other Leaders
It is in line with this learning and this desire to move the country forward and direct it towards the construction of an educational framework responding to real needs and respecting the national conditions of deep local and regional reforms and integration as a new nation through a rational strategy and national industrial model with options for socialism

Look up details

Extract: Rooted in history, the BRI carries forward the Silk Road spirit
At around 140 BC during China’s Han Dynasty, Zhang Qian, a royal emissary, made a journey to the West from Chang’an (present-day Xi’an in Shaanxi Province), opening an overland route linking the East and the West. Centuries later, in the years of the Tang, Song and Yuan dynasties, silk routes boomed both over land and at sea, facilitating trade between the East and the West. In the early 15th century, Zheng He, the famous Chinese navigator of the Ming Dynasty, made seven voyages to the Western Seas, which boosted trade along the maritime silk routes.
For thousands of years the ancient silk routes served as major arteries of interaction, spanning the valleys of the Nile, the Tigris and Euphrates, the Indus and Ganges, and the Yellow and Yangtze rivers. They connected the birthplaces of the Egyptian, Babylonian, Indian and Chinese civilizations, the lands of the believers of Buddhism, Christianity and Islam, and the homes of peoples of different nationalities and races. These routes increased connectivity among countries on the Eurasian continent, facilitated exchanges and mutual learning between Eastern and Western civilizations, boosted regional development and prosperity, and shaped the Silk Road spirit characterized by peace and cooperation, openness and inclusiveness, mutual learning and mutual benefit.
The BRIC acronym was created in 2001 by Jim O’Neill, a Goldman Sachs economist. The BRIC countries were established in 2014. The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) was established in 2014 by the BRIC countries.
The BRIC acronym stands for fast-growing economies that O’Neill predicted would dominate the global economy by 2050. The BRIC countries were formalized in 2006 during the first BRIC Foreign Ministers’ Meeting in New York City. The first BRIC summit was held in Yekaterinburg, Russia on June 16, 2009. The BRIC countries became a formal institution in 2010.
Xi Jinping is the 7th President of the People’s Republic of China and the 18–20th General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party. He has been the paramount leader of China since 2012. He has made 42 international trips to 69 countries. Xi Jinping was born on June 15, 1953. He is also the chairman of the Central Military Commission (CMC).
In March 2013, President Xi Jinping proposed the vision of a global community of shared future. In September, President Xi Jinping announced the BRI in September 2013 during his visit to Kazakhstan and in October that year, he raised the initiatives of joining with others to build a Silk Road Economic Belt and a 21st Century Maritime Silk Road (Belt and Road Initiative, or BRI).

The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is a massive infrastructure of China global development strategy based on economic development projects. It was originally devised to link East Asia and Europe through physical infrastructure. The BRI has poured hundreds of billions of dollars to power the construction of: Bridges, Ports, Highways, Power plants, Telecoms projects. The BRI has been used in Asia, Latin America, Africa, and parts of Europe.
“The Belt and Road Initiative is a creative development that takes on and carries forward the spirit of the ancient silk routes – two of the great achievements in human history and civilization. It enriches the ancient spirit with the zeitgeist and culture of the new era, and provides a platform for building a global community of shared future.
Since its launch 10 years ago, thanks to the combined efforts of all parties, cooperation under the BRI framework has expanded beyond the borders of China to become an international effort. It has evolved from ideas into actions, from a vision into reality, and from a general framework into concrete projects. It has been welcomed by the international community both as a public good and a cooperation platform, and has achieved solid results ensuring that the efforts of building a global community of shared future deliver
Over the past decade, BRI cooperation has delivered real gains to participating countries. It has contributed to the sound development of economic globalization and helped to resolve global development challenges and improve the global governance system. It has also opened up a new path for all humanity to realize modernization, and ensured that the efforts of building a global community of shared future are delivering real results.”
As of August 2023, 155 countries had signed up to the BRI. The participating countries include almost 75% of the world’s population and account for more than half of the world’s GDP. The BRI’s goal is to invest in more than 150 countries and international organizations. The BRI’s planned completion date is 2049. The BRI started as a program for Chinese companies to build transportation, energy, and other infrastructure overseas. The BRI is funded by Chinese development bank loans.

Russian leader Vladimir Putin was given the red carpet treatment at a global summit in Beijing, as China and Russia deepen their solidarity. Hosted by China’s President Xi Jinping, the meeting celebrated 10 years of his signature foreign and economic policy, the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
President Putin was the Guest of Honor at the 2023 Belt and Road Forum was held in Beijing, China.
In an interview with Chinese state media on Monday, October 16, 2023, Putin said Xi “calls me his friend, and I call him my friend.”
The Russian president added that there is a saying, “Tell me who your friend is, and I will tell you who you are.” He went on: “Therefore, if I now praise Chairman Xi Jinping, I will feel somehow uncomfortable – it’s like I’m praising myself. So I’ll try to be objective.”
Putin described his Chinese counterpart as “one of the recognized world leaders” who does not “make a momentary decision based on some current situation, he assesses the situation, analyzes and looks into the future.”
Putin Praising the Belt and Road Initiative following the in-depth talks talk that Putin and Xi shared together on October 18, 2023. In the Russian president’s speech at the forum, he praised Xi for the successes of the Belt and Road Initiative, saying: “Our Chinese friends did it.”
Speaking to 1,000 delegates representing over 130 countries, Putin said he agreed with Chinese President Xi Jinping that the Belt and Road idea “folds logically within multilateral efforts” to increase global cooperation. “In the European part of Russia, we form an international north-south corridor.
President Vladimir Putin on Wednesday praised Chinese President Xi Jinping for the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and invited global investment in the Northern Sea route which he said could deepen trade between east and west.
Speaking on his second known trip outside the former Soviet Union since the Ukraine war, Putin thanked the Chinese leader for his invitation and said Russia could play a key role in China’s modern day revival of the ancient Silk Road.
China’s success was “really important for us,” he added. “Russia and China, like most countries of the world, share the desire for equal, mutually beneficial cooperation in order to achieve universal sustainable and long-term economic progress and social well-being, while respecting the diversity of civilization and the right of each state to its own development model.”
Family photo of President Xi Jinping, Madame Peng Liyuan and foreign leaders with their spouses attending the Third #BeltandRoadForum for International Cooperation. pic.twitter.com/BZbWgGQxaB
— Hua Chunying 华春莹 (@SpokespersonCHN) October 17, 2023
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is a Chinese infrastructure development strategy that aims to connect Asia, Africa, and Europe through land and maritime networks. The BRI was launched in 2013 by President Xi Jinping. The planned completion date is 2049. The BRI includes the Silk Road Economic Belt for the land part and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road for the naval part. The BRI has invested in more than 150 countries and over 30 international organizations.
The BRI’s goals include:
The BRI’s five major goals are: Policy coordination, Facilities connectivity, Unimpeded trade, Financial integration, People-to-people bond.
The BRI involves China financing billions of dollars of investment in roads, railways, and other infrastructure across Eurasia and Africa. China claims the BRI has created 420,000 jobs and lifted 40 million people out of poverty.
The BRI is also known as the One Belt One Road (OBOR). It involves investing in more than 150 countries and international organizations.
Some countries that are part of the BRI include: Brunei Darussalam, Bulgaria, Burundi.
The United States has criticized the BRI, with President Biden calling it a “debt and noose agreement”. The US opposition to the BRI is commonly understood as a competition between the two powers for economic advantage and international influence. The European Union and the United States have their own development schemes, known as B3W “Build Back Better” and “Globally Connected Europe”.
The BRI has been controversial since its inception. Some of the opposition to the BRI includes:
Some analysts see the BRI as a disturbing expansion of Chinese power. US military leaders have sharply criticized the BRI. Former defense secretary Jim Mattis said, “In a globalized world, there are many belts and many roads, and no one nation should put itself into a position of dictating ‘one belt, one road’”.
The US has been critical of the BRI for almost a decade. The US has been using investments, loan programs, public-private partnerships, and technical assistance to counter the BRI. The Biden-Harris administration announced an infrastructure financing mechanism for low- and middle-income countries. The US also plans to invest in five to 10 large infrastructure projects around the world.
The US wants to pressure China to change its BRI practices and provide an alternative that promotes sustainable infrastructure and high environmental and anticorruption standards. The US and its partners revealed an economic corridor linking India, the Middle East, and Europe.

/ Home / 2023年10月11日 / Belt and Road Initiative, BRI, China, finance, 一带一路, 中国, 带路, 融资
The State Council Information Office of the People’s Republic of China
October 2023
Contents
Preamble
III. Promoting All-Round Connectivity in Multiple Fields
Conclusion
Over two millennia ago, inspired by a sincere wish for friendship, our ancestors travelled across grasslands and deserts to create a land Silk Road connecting Asia, Europe and Africa, leading the world into an era of extensive cultural exchanges. More than 1,000 years ago, our ancestors set sail and braved the waves to open a maritime Silk Road linking the East and the West, beginning a new phase of closer communication among peoples.
Spanning thousands of miles and years, the ancient silk routes were not only routes for trade but also roads for cultural exchanges. They made a great contribution to human progress. In the 1980s, the United Nations and some countries began to envisage the Eurasian Land Bridge, the Silk Road Initiative, and other plans, reflecting a common wish to engage in communication and cooperation.
In March 2013, President Xi Jinping proposed the vision of a global community of shared future; in September and October that year, he raised the initiatives of joining with others to build a Silk Road Economic Belt and a 21st Century Maritime Silk Road (Belt and Road Initiative, or BRI). The Belt and Road Initiative is a creative development that takes on and carries forward the spirit of the ancient silk routes – two of the great achievements in human history and civilization. It enriches the ancient spirit with the zeitgeist and culture of the new era, and provides a platform for building a global community of shared future.
Since its launch 10 years ago, thanks to the combined efforts of all parties, cooperation under the BRI framework has expanded beyond the borders of China to become an international effort. It has evolved from ideas into actions, from a vision into reality, and from a general framework into concrete projects. It has been welcomed by the international community both as a public good and a cooperation platform, and has achieved solid results.
Over the past decade, BRI cooperation has delivered real gains to participating countries. It has contributed to the sound development of economic globalization and helped to resolve global development challenges and improve the global governance system. It has also opened up a new path for all humanity to realize modernization, and ensured that the efforts of building a global community of shared future are delivering real results.
The Chinese government is publishing this white paper to present the achievements of the BRI during the past 10 years. It will give the international community a better understanding of the value of the initiative, facilitate high-quality cooperation under it, and ultimately deliver benefits to more countries and peoples.
Proposed by China but Belonging to the Whole World
The world today is going through profound change on a scale unseen in a century. Problems and challenges continue to threaten the progress of human civilization. In response to a changing global situation and the expectations of the international community, and with the future and overall interests of humanity in mind, China proposed the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). Committed to the Silk Road spirit, a great heritage of human civilization, the BRI connects the past, the present, and the future. This initiative was launched by China, but it belongs to the world and benefits the whole of humanity.
Rooted in history, the BRI carries forward the Silk Road spirit
At around 140 BC during China’s Han Dynasty, Zhang Qian, a royal emissary, made a journey to the West from Chang’an (present-day Xi’an in Shaanxi Province), opening an overland route linking the East and the West. Centuries later, in the years of the Tang, Song and Yuan dynasties, silk routes boomed both over land and at sea, facilitating trade between the East and the West. In the early 15th century, Zheng He, the famous Chinese navigator of the Ming Dynasty, made seven voyages to the Western Seas, which boosted trade along the maritime silk routes.
For thousands of years the ancient silk routes served as major arteries of interaction, spanning the valleys of the Nile, the Tigris and Euphrates, the Indus and Ganges, and the Yellow and Yangtze rivers. They connected the birthplaces of the Egyptian, Babylonian, Indian and Chinese civilizations, the lands of the believers of Buddhism, Christianity and Islam, and the homes of peoples of different nationalities and races. These routes increased connectivity among countries on the Eurasian continent, facilitated exchanges and mutual learning between Eastern and Western civilizations, boosted regional development and prosperity, and shaped the Silk Road spirit characterized by peace and cooperation, openness and inclusiveness, mutual learning and mutual benefit.
Symbolizing communication and cooperation between the East and the West, the millennia-old silk routes demonstrated that by upholding solidarity and mutual trust, equality and mutual benefit, inclusiveness and mutual learning, and win-win cooperation, countries of different ethnic groups, beliefs and cultural backgrounds could share peace and achieve development together. The Silk Road spirit is consistent with the ideal of “all states joining together in harmony and peace” long upheld by the Chinese nation, with the Chinese people’s principles of amity, good neighborliness and “helping others to succeed while seeking our own success”, and with the call of the times for peace, development and win-win cooperation.
The Communist Party of China is a major political party with a global vision, and China is a major country pursuing peaceful development. The BRI, which carries forward the Silk Road spirit in the new era, evokes the pleasant memories of the past and has fired many countries’ enthusiasm for connectivity.
The BRI pays respect to history and tries to recreate the bustling scenes of untiring envoys and businessmen over land and countless ships calling at ports along the ancient silk routes. It is also navigating a way to the future by drawing wisdom and strength from the ancient silk routes and the Silk Road spirit. Enlightened by history, we will continue to move forward and integrate the Chinese Dream with the world’s dreams, in order to realize the aspiration of all peoples for exchanges between civilizations, peace and tranquility, common development, and better lives.
In response to reality, the BRI resolves problems in development
Development holds the master key to solving all problems. Economic globalization has given strong momentum to the world economy. Over 500 years ago, after the ancient silk routes had been interrupted for more than a half century, the Age of Discovery arrived, fundamentally changing the course of human society. Since the advent of modern times, technological revolutions and development of the productive forces have made economic globalization a surging historical trend. In particular, since the 1990s, the rapid advance of economic globalization has greatly facilitated trade, investment, flows of people, and technological progress, making an important contribution to the progress of human society.
However, the economic globalization dominated by a few countries has not contributed to the common development that delivers benefits to all. Instead, it has widened the wealth gap between rich and poor, between developed and developing countries, and within developed countries. Many developing countries have benefited little from economic globalization and even lost their capacity for independent development, making it hard for them to access the track of modernization. Certain countries have practiced unilateralism, protectionism and hegemonism, hampering economic globalization and threatening a global economic recession.
It is imperative to address such global problems as sluggish economic growth, shortcomings in economic governance, and imbalanced economic development. It is no longer acceptable that only a few countries dominate world economic development, control economic rules, and enjoy development fruits.
The BRI targets development not only for China but for the world at large. Economic globalization remains an irreversible trend. It is unthinkable for countries to return to a state of seclusion or isolation. However, economic globalization must undergo adjustments in both form and substance. It should be made more open, inclusive, balanced and beneficial to all.
China has not only benefited from economic globalization but also contributed to it. As an active participant in economic globalization, China has achieved rapid economic growth through positive interactions with the rest of the world and explored a unique path towards modernization, expanding the options for other developing countries to achieve modernization. China’s rapid economic growth and steady progress in reform and opening up has provided a strong driving force for global economic stability and growth as well as an open world economy.
China has been a firm advocate and defender of economic globalization. The BRI dovetails with the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development in concept, measures and goals. A major step taken by China, the BRI aims to promote higher-quality development through higher-standard opening up, and share China’s development opportunities with the rest of the world. The BRI is also a Chinese solution to global development issues, which aims to advance modernization in participating countries in tandem, make economic globalization more dynamic, inclusive and sustainable, and ensure that more of the fruits will be shared more equitably by people across the world.
Today, the world is moving ever closer towards greater multipolarity, economic globalization, and cultural diversity, and becoming increasingly information-orientated in the process. Countries are more frequently connected and closely interdependent than at any time in the past. It is increasingly clear that humanity is a community of shared future in which everyone’s interests are inseparably entwined.
However, a growing deficit in peace, development, security and governance, together with interwinding conventional and non-conventional security issues such as regional conflicts, arms races, food security, terrorism, cyber-attacks, climate change, energy crises, major infectious diseases, and artificial intelligence problems, poses a grave threat to the beautiful planet on which all humans live.
In the face of emerging global difficulties and challenges, human society needs new ideas, new concepts, and a more just, equitable, balanced, resilient and effective global governance system. What kind of world to build and which way to take to create a brighter future are issues that have a bearing on every country and every person. We must respond to the challenges presented by the times and make the right historic choice.
As a major developing country that meets its responsibilities, China keeps in mind the future and the common interests of humanity. China has therefore proposed building a global community of shared future, with the goal of creating an open, inclusive, clean and beautiful world that enjoys lasting peace, universal security and common prosperity, charting a bright future for human development.
The ultimate goal of the BRI is to help build a global community of shared future. As an important public good for improving global governance, the initiative provides a platform for turning the vision into reality. The BRI involves countries in different regions, at different development stages, and with different cultures. It transcends differences in ideologies and social systems. It enables different countries to share opportunities, realize common development and prosperity, and build a community of shared interests, responsibility and destiny characterized by mutual political trust, economic integration and cultural inclusiveness. As a practical means of building a global community of shared future, the BRI has created new understanding and inspired the imagination of the world, and contributed new ideas and new approaches to international exchanges. It will produce a fairer and more equitable global governance system, and take humanity to a better future.
The BRI is in alignment with the concept of a global community of shared future. It promotes and puts into action ideas that are relevant to the present era, the world, development, security, openness, cooperation, civilization, and governance. It provides not only a conceptual framework but also a practical roadmap for all nations to achieve shared development and prosperity.
The BRI is founded on the principles of extensive consultation, joint contribution, and shared benefits. It advocates win-win cooperation in pursuit of the greater good and shared interests. It emphasizes that all countries are equal participants, contributors and beneficiaries, and encourages economic integration, interconnected development, and the sharing of achievements.
The principle of extensive consultation signifies that the BRI is not a solo endeavor by China, but a collaborative effort involving all stakeholders. This principle promotes and activates authentic multilateralism, encouraging collective decision-making while fully respecting the varying levels of development, economic structures, legal systems, and cultural traditions of different nations. It emphasizes equal participation, effective communication, collective wisdom, freedom from any political or economic preconditions, and voluntary engagement to foster maximum consensus. Irrespective of size, strength and wealth, all countries participate on an equal footing and can provide opinions and proposals in bilateral and multilateral cooperation.
Under this principle, economies at different stages of development will reinforce bilateral or multilateral communication, jointly identify and establish innovative cooperation mechanisms, and provide a platform for dialogue, cooperation and participation in global governance.
The principle of joint contribution highlights that the BRI is not one of China’s international aid programs or geopolitical tool, but a collaborative effort for shared development. It aims to align with existing regional mechanisms rather than becoming their substitute and leverage complementary strengths. This principle emphasizes the participation of all parties involved, substantial coordination with the development strategies of relevant countries and regions, and the identification and utilization of their respective development potential and comparative strengths. The objective is to collectively create new opportunities, driving forces, and development space while achieving complementary and interactive growth by capitalizing on each party’s strengths and capabilities.
To promote extensive participation, this principle encourages countries and businesses to engage through various forms such as bilateral cooperation, third-party market cooperation and multilateral cooperation, thereby creating synergy for development. This principle values market forces and promotes market-oriented operations to further the interests and meet the expectations of all parties involved. In this context, businesses play a central role as the main actors, while the government’s responsibility lies in building platforms, establishing mechanisms, and providing policy guidance. China’s key role in BRI cooperation stems from its economic size, market scale, experience in infrastructure construction, capacity to produce low-cost, high-quality, high-performance equipment, and comprehensive strengths in industry, capital, technology, talent and management.
The principle of shared benefits underscores the importance of win-win cooperation. It aims to identify common interests and grounds for cooperation, meet the development needs of all parties, and address the real concerns of the people. This principle emphasizes sharing development opportunities and outcomes among all participating countries, ensuring that none of them is left behind. Most participants are developing countries, all seeking to leverage collective strengths to address challenges such as inadequate infrastructure, lagging industrial development, limited industrialization, insufficient capital and technology, and a shortage of skilled workers, to promote their own economic and social development.
Under the BRI framework, China pursues the greater good and shared interests, with the former taking precedence, by providing assistance to partner countries within its capabilities and genuinely supporting other developing countries to accelerate development. Simultaneously, through BRI cooperation, China aims to foster all-round opening up by building connections with other countries over land and sea while creating synergy between its eastern and western regions. It seeks to build a more advanced open economy and create a double development dynamic with the domestic economy as the mainstay and the domestic economy and international engagement providing mutual reinforcement.
The BRI is committed to open, green and clean cooperation towards inclusive and sustainable development. It has zero tolerance for corruption and promotes steady and high-quality growth.
The BRI is a public road open to all, not a private path owned by any single party. It is free from geopolitical calculations. It does not aim to create an exclusive club, nor does it target at any party. It does not form cliques based on specific ideological standards. It has no intention of establishing military alliances. Countries from Eurasia, Africa, the Americas, and Oceania are all welcome to participate in the initiative, regardless of their political system, historical background, culture, development stage, ideology, or religious beliefs, as long as they seek common development. All participants uphold principles of openness and inclusiveness, while firmly opposing protectionism, unilateralism and hegemonism, and working together to create an all-round, three-dimensional landscape of interconnectivity. The goals are to develop a new model of cooperation based on win-win outcomes, shared responsibility, and collective participation, build a global network of partnerships, and nurture a harmonious coexistence for humanity.
The BRI embraces the global trend of green and low-carbon development, emphasizes respecting and protecting nature and following its laws, and respects the right of all parties to pursue sustainable and eco-friendly growth.
Based on a shared commitment to eco-environmental considerations, the parties involved have carried out policy dialogues, and shared ideas and achievements in green development. Through closer cooperation in areas such as green infrastructure, renewable energy, eco-friendly transport, and sustainable finance, all parties work together to broaden consensus and take concrete steps towards green development. The ultimate goal is to establish a resource-efficient, eco-conscious and low-carbon Silk Road, thereby making a significant contribution to protecting the eco-environment, achieving peak carbon and neutrality goals and addressing climate change.
Leveraging its expertise in renewable energy, energy conservation, environmental protection and clean production, and employing Chinese technology, products and experience, China actively promotes BRI cooperation in green development.
Clean governance is considered an intrinsic and necessary condition for the steady and sustained development of the BRI, with a commitment to transparency in cooperation. All participants joined to combat corruption, strengthening their legal systems and mechanisms, harmonizing their laws and regulations, and fostering international cooperation. Furthermore, all participants stand united against all forms of corruption and other international criminal activities, and work consistently to combat commercial bribery. This ensures that financial resources and projects are managed with integrity and efficiency, leading to greater outcomes and making BRI cooperation an example of clean governance.
In April 2019, together with relevant countries, international organizations, and representatives from the business and academic communities, China launched the Beijing Initiative for the Clean Silk Road. This initiative calls for a clean Silk Road characterized by extensive consultation, joint contribution, and shared benefits. Chinese companies expanding globally are committed to compliance and lawful operations, adhering to the laws of both China and the host countries and to international norms. They have particularly heightened their capacity to mitigate overseas operational risks, strengthening project supervision and management to ensure the delivery of clean, cost-efficient and high-quality projects.
State-owned enterprises (SOEs) directly under the central government have released 868 guidelines of compliance in key areas, and defined 5,000-plus job compliance responsibilities; SOEs and financial institutions directly under the central government and their branches have formulated and updated more than 15,000 rules for managing overseas operations. In November 2020, more than 60 Chinese enterprises engaged in extensive BRI cooperation joined in launching the Integrity and Compliance Initiative for BRI Enterprises.
The BRI aims at high standards, sustainability, and better lives by raising cooperation standard, investment effectiveness, supply quality, and development resilience, delivering real and substantive results for all participants.
The BRI introduces universally accepted rules and standards to guide business practices in project tendering, procurement, development and operation. It promotes high-standard cooperation and construction in various sectors. It advocates establishing free trade zones in alignment with international rules and standards, and implementing policies to promote trade and investment liberalization and facilitation to a higher level. This will ensure safe, smooth and orderly flows of people, goods, funds and data, and enable greater interconnectivity and deeper exchanges and cooperation. The approach emphasizes world-class standards, practicality, and cost-effectiveness. Pilot projects precede wider implementation, and participating countries are encouraged to adopt rules and the path adapted to their national conditions. China has established a high-level leadership organization and issued policy documents to consistently improve BRI design and implementation.
In alignment with the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the BRI promotes coordinated economic, social, and eco-environmental development. Its aims are to address the root causes and obstacles that hinder development and boost the self-driven development of participating countries. It strives to achieve lasting, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, integrating sustainable development principles into project selection, implementation and management. Following international practices and debt sustainability principles, it is working to create a long-term, stable, sustainable and risk-controlled investment and financing system with innovative models and diverse channels in order to establish a stable, transparent and high-quality funding guarantee system that ensures commercial and fiscal sustainability. No participating country has fallen into a debt crisis as a result of BRI cooperation.
The BRI takes a people-centered approach, with the focus on poverty eradication, job creation, and improvement of people’s wellbeing to ensure that the benefits of cooperation reach all individuals. Deeper cooperation is encouraged in areas such as public health, poverty reduction, disaster mitigation, green development, science and technology, education, culture, arts, and health care. Closer exchanges are promoted among political parties, social organizations, think tanks, youth, women, and sub-national communities. These efforts aim to create projects that are grounded in the needs of the people, increasing their sense of gain and fulfillment. China actively promotes small-scale yet impactful projects through foreign aid, benefiting people’s lives. From Asia to Africa, Latin America to the South Pacific, the construction of roads, railways, schools, hospitals and agricultural facilities contributes to poverty reduction and improves the people’s wellbeing in participating countries.
An initiative towards progress, cooperation and inclusiveness, the BRI pursues development, promotes win-win outcomes, and inspires hope. It aims to deepen understanding and trust, strengthen comprehensive exchanges, and ultimately achieve common development and shared prosperity.
A path to peace. Peace is a prerequisite for development, while development serves as the foundation for peace. The BRI goes beyond the law of the jungle and the hegemonic order based on power struggles. It rejects zero-sum thinking and discards the Cold War mentality of ideological rivalry and geopolitical competition. Instead, it paves the way for peaceful development, and aims to offer a fundamental approach to lasting peace and universal security. Under the BRI, nations respect each other’s sovereignty, dignity, territorial integrity, development path, social system, core interests, and major concerns. As the initiator of the BRI, China passionately campaigns for the establishment of a new model of international relations characterized by mutual respect, equity, justice, and win-win cooperation. It is committed to building partnerships based on dialogue rather than confrontation, and friendship rather than alliance, and to fostering a new vision of common, comprehensive, cooperative and sustainable security. These efforts help to create a peaceful and stable development environment.
A path to prosperity. The BRI is committed to building a prosperous future that diverges from the exploitative colonialism of the past, avoids coercive and one-sided transactions, rejects the center-periphery model of dependency, and refuses to displace crisis onto others or exploit neighbors for self-interest. Instead, it aims to achieve win-win outcomes and shared development and prosperity. Under the BRI, all parties will prioritize development as the common goal, leveraging their respective resources and potential advantages, igniting their own growth engines, growing their capacity for independent development, and collectively creating more opportunities and space for development. This collaborative effort aims to foster new centers and impetus for global economic growth, drive inclusive growth, and bring global development into a balanced, coordinated and inclusive new stage.
A path to openness. The BRI represents an open and inclusive collaborative process that transcends national borders, ideological differences, developmental disparities, social system variations, and geopolitical conflicts. It is not aimed at designing a new international system, but rather supplementing and improving the existing mechanisms. All parties involved uphold the core values and fundamental principles of the multilateral trading system. Together, participants will establish an open and cooperative platform, safeguard and promote an open global economy, create an environment conducive to open development, construct a fair, equitable and transparent system of international trade and investment rules, and advance cooperation based on win-win outcomes, shared responsibility and collective participation. The BRI facilitates the orderly flow of production factors, the efficient allocation of resources, deep integration of markets, and liberalization and facilitation of trade and investment, and ensures the stable performance and smooth operation of global industrial and supply chains. It aims to build an economic globalization that is open, inclusive, balanced, and beneficial to all.
A path to innovation. Innovation serves as a critical driving force for progress. The BRI is dedicated to innovation-led development, harnessing the opportunities presented by digital, internet-based and smart development. It explores new business forms, technologies and models, seeking out fresh sources of growth and innovative development pathways to propel transformative advancements for all involved. Participants collaborate to connect digital infrastructure, build the Digital Silk Road, strengthen innovative cooperation in cutting-edge fields, and promote the deep integration of science, technology, industry and finance. These efforts aim to optimize the environment for innovation, gather innovative resources, foster a regional ecosystem of collaborative innovation, and bridge the digital divide, injecting strong momentum into common development.
A path to social progress. The BRI champions equality, mutual learning, dialogue, and inclusiveness among civilizations. It upholds the shared values of peace, development, equity, justice, democracy and freedom. It transcends barriers between cultures through exchanges, resolves conflicts through mutual understanding, and rejects superiority while promoting coexistence. It encourages civilizations to appreciate their differences, seek common ground, and learn from one another. Parties involved will establish multitiered mechanisms for people-to-people cooperation, create more platforms and channels, and facilitate exchanges across various fields. These efforts aim to reinforce mutual understanding, respect and trust among nations, broaden consensus on ideas and values, and achieve new human progress.
To promote greater connectivity through BRI cooperation, we have continued to facilitate policy coordination, infrastructure connectivity, unimpeded trade, financial integration, and closer people-to-people ties, by orienting towards “hard connectivity” in infrastructure, bolstering “soft connectivity” through harmonized rules and standards, and strengthening people-to-people bonds. As its scope expands, the BRI has become the world’s largest platform for international cooperation, with the broadest coverage.
Policy coordination underpins BRI cooperation. China has worked with participating countries and international organizations to establish a multilevel policy coordination and communication mechanism for aligning development strategies, technological and economic policies, and administration rules and standards. Under this mechanism, plans and measures for regional cooperation have been formulated through joint efforts to facilitate and speed up cooperation, making the BRI an important collaborative framework for international exchanges.
Strategy and policy coordination is expanding in scope. At the global level, the 193 UN member states unanimously agreed to incorporate the Belt and Road Initiative in the UN resolution passed at the 71st United Nations General Assembly in November 2016. In March 2017, the United Nations Security Council adopted Resolution 2344, calling for stronger regional economic cooperation through the BRI, among other initiatives. The United Nations Development Programme and the World Health Organization (WHO) have signed BRI cooperation agreements with China. At the World Trade Organization (WTO), China’s efforts have facilitated the conclusion of the negotiations on the text of the Investment Facilitation for Development Agreement, with a view to establishing a coordinated and unified investment management system covering more than 110 countries and regions to encourage BRI cooperation on investment.
At regional and multilateral levels, the BRI has supported regional integration and global development by aligning with plans such as the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity 2025, the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific, the African Union’s Agenda 2063, and the European Union’s Strategy on Connecting Europe and Asia.
At the bilateral level, the BRI has succeeded in coordinating with a wide range of strategies and initiatives, including Russia’s Eurasian Economic Union framework, Kazakhstan’s Bright Road economic policy, Turkmenistan’s strategy of reviving the Silk Road, Mongolia’s Steppe Road plan, Indonesia’s Global Marine Fulcrum initiative, the Philippines’ Build Better More program, Vietnam’s Two Corridors and One Economic Circle plan, South Africa’s Economic Reconstruction and Recovery Plan, Egypt’s Suez Canal Corridor Project, and Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030. By June 2023, China had signed more than 200 BRI cooperation agreements with more than 150 countries and 30 international organizations across five continents, yielding a number of signature projects and small-scale yet impactful projects.
A long-term mechanism for policy coordination is largely in place. Multilevel channels for regular communication among different parties have been opened up on different platforms. This has been made possible through top-down driven diplomatic efforts led by heads of state, with support from intergovernmental strategic communication and local and interdepartmental policy coordination, and with cooperation projects carried out by enterprises and social organizations.
China has hosted the Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation twice, providing an important platform for participating countries and international organizations to expand exchanges, increase mutual trust, and strengthen ties. The first forum in 2017 welcomed heads of state and government from 29 countries, and more than 1,600 representatives from 140-plus countries and 80-plus international organizations, yielding a total of 279 deliverables in five categories. At the second forum held in 2019, 40 leaders, including heads of state and government from 38 countries, the UN secretary-general and the International Monetary Fund’s managing director, attended the Leaders’ Roundtable. More than 6,000 representatives participated, from over 150 countries and 92 international organizations, yielding 283 deliverables in 6 categories.
Multilateral cooperation is driving forward. Under the BRI framework, Chinese and foreign partners have launched 20-plus multilateral dialogue and cooperation mechanisms in professional domains such as railways, ports, energy, finance, taxation, environmental protection, disaster prevention and relief, think tanks, and the media, attracting a growing number of participants. BRI participating countries have also expanded practical cooperation through major multilateral platforms such as China-ASEAN (10+1) Cooperation, Forum on China-Africa Cooperation, China-Arab States Cooperation Forum, Forum of China and the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States, China-Pacific Island Countries Economic Development and Cooperation Forum, China-Central and Eastern European Countries Cooperation, World Economic Forum, Boao Forum for Asia, and CPC and World Political Parties Summit.
Rules and standards are being coordinated. Cooperation on standardization has advanced to new levels. As of June 2023, China had signed 107 documents with standardization bodies in 65 countries such as Pakistan, Russia, Greece, Ethiopia, and Costa Rica and also with regional and international organizations, in areas covering civil aviation, climate change, agri-food, building materials, electric vehicles, oil and gas pipelines, logistics, small hydropower stations, oceanography, and surveying and mapping.
The Standard Information Platform Contributed by the Belt and Road Countries provides overviews of standards information in 149 partner countries, and full-text search services for standards catalogues regarding 59 countries and 6 regional and international standardization organizations, serving as a bridge for participating countries. Chinese standards in foreign language versions have been supplied in larger quantities. Nearly 1,400 national standards and more than 1,000 industry standards have been published in foreign languages.
In May 2022, the Asian-African Legal Consultative Organization opened a regional arbitration center in Hong Kong, providing solutions for multilateral disputes in BRI cooperation.
China has continued to strengthen cross-border accounting and auditing regulatory cooperation with 22 countries and regions including Russia, Malaysia and Singapore, providing institutional guarantees for expanding cross-border investment and financing channels.
The BRI prioritizes connectivity of infrastructure. Based on a framework comprising “six corridors, six routes, and multiple countries and ports”, a multitiered and multidimensional infrastructure network is taking shape. Basic connectivity over land, maritime, air and cyberspace is in place, laying solid foundations for deeper cooperation in trade and industrial capacity, and strengthening cultural and people-to-people exchanges.
The construction of economic corridors and international routes is making substantial progress. Participating countries have pressed forward with the creation of international arterial routes, building an infrastructure network that connects subregions in Asia as well as the continents of Asia, Europe and Africa.
Major projects along the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor are under way. The Peshawar-Karachi Motorway (Sukkur-Multan section), the Karakoram Highway Phase II (Havelian-Thakot section), and the Lahore Orange Line Metro are all open to traffic. Coal-fired power plants such as Sahiwal, Port Qasim, Thar, and Hub are operating safely and steadily; the Mehra DC transmission project is operational; and the Kalot Hydropower Station is connected to the power grid. Rashakai Special Economic Zone has reached the stage of comprehensive development.
Along the New Eurasian Land Bridge, the Belgrade-Novi Sad section of the Hungary-Serbia Railway in Serbia became operational in March 2022, and track-laying has started on the Budapest-Kelebija section in Hungary. The Peljesac Bridge in Croatia has celebrated its first anniversary of opening to traffic. The Western Europe-Western China Highway has been completed. The Smokovac-Matesevo section of the Bar-Boljare Highway in Montenegro has been completed and is open to traffic.
Along the China-Indochina Peninsula Economic Corridor, the China-Laos Railway has been completed and is providing sound service, and its role as a golden transport channel is becoming increasingly prominent. The Jakarta-Bandung High-speed Railway, the flagship project of BRI cooperation between China and Indonesia, has achieved an operational speed of 350 km per hour. The contract for the China-Thailand Railway Phase I (Bangkok-Nakhon Ratchasima section) was signed online, and 11 sections of the construction project have started, including one that has been completed.
Along the China-Mongolia-Russia Economic Corridor, the Heihe-Blagoveshchensk Highway Bridge and the Tongjiang-Nizhneleninskoye Railway Bridge, connecting China and Russia, have opened to traffic. The China-Russia eastern natural gas pipeline is fully operational. China, Russia and Mongolia have officially launched a feasibility study on the upgrading and development of the central-route railway of the China-Mongolia-Russia Economic Corridor.
Along the China-Central Asia-West Asia Economic Corridor, the China-Kyrgyzstan-Uzbekistan Highway is in full operation. The China-Central Asia Gas Pipeline is fully operational. The grain and oil rail transport lines between North Kazakhstan and China are operating in conjunction with the China-Europe Railway Express.
Along the Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor, the China-Myanmar Crude Oil and Gas Pipeline has been completed and entered service. The feasibility study on the Muse-Mandalay section of the China-Myanmar Railway has been completed, and the feasibility study on the Mandalay-Kyaukphyu section has been launched. Construction projects in Bangladesh, including the Bangladesh-China Friendship Bridge and the Dohazari-Cox’s Bazar rail route, have made good progress.
The Mombasa-Nairobi Standard Gauge Railway in Kenya connects Mombasa, the largest port in East Africa, and Nairobi, the capital of Kenya. It extends further northwest to Suswa. The line is 592 kilometers long. It utilizes Chinese standards, technology, equipment, and project management. It is an important success story in BRI cooperation between China and Kenya, and is hailed as a route of friendship, of win-win cooperation, of development and prosperity, and of eco-environmental protection.
The Mombasa-Nairobi Railway is the largest infrastructure project undertaken in Kenya since independence. Since it opened in 2017, the railway has had a positive impact on Kenya’s economic and social development and the people’s wellbeing; it has also significantly reduced the logistics costs of products from the inland regions of East Africa exported through the Mombasa Port. As of August 31, 2023, the railway is operating an average of 6 passenger trains per day; a total of 11 million passengers have been carried, and the average occupancy rate is above 95 percent; an average of 17 freight trains operate daily, and a total of 28 million tonnes of goods have been transported. According to Kenyan government estimates, the railway has added 2 percent to Kenya’s economic growth.In the construction and operation of the Mombasa-Nairobi Railway, Chinese enterprises have supported technology transfer and provided training to local employees.
During the construction period, more than 30,000 local employees received orientation training, and every year a number of young Kenyans were selected to participate in training and academic education in China. Since the opening of the railway, Chinese companies have adopted tailored training methods for different people, professions and posts, and have trained 1,152 professionals for Kenya.
In Africa, railways such as the Mombasa-Nairobi Railway and the Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway are now operational and have become important drivers of in-depth development not only in East Africa but across the entire continent.
Maritime connectivity is steadily improving. Cooperation is expanding in shipping among the ports of participating countries, and the efficiency of cargo transportation has seen notable increase.
The annual cargo throughput of the Port of Piraeus in Greece has increased to above 5 million twenty-foot equivalent units (TEUs), making it the fourth largest TEU port in Europe and a leading TEU port in the Mediterranean.
The Gwadar Port in Pakistan has seen major progress and is marching towards the goal of becoming a logistics center and industrial base.
Preliminary work is currently under way on the Kyaukphyu Deep-sea Port project in Myanmar, including geological exploration and environmental and social assessment.
The annual throughput of bulk cargo at Hambantota Port in Sri Lanka has increased to 1.21 million tonnes.
The Vado Gateway terminal has become the first semi-automatic terminal operating in Italy.
The Lekki Deep-sea Port in Nigeria has been completed and entered service, becoming a major modern deepwater port in Central and Western Africa.
The Silk Road Maritime network has continued to expand. By the end of June 2023, it had reached 117 ports in 43 countries, and more than 300 well-known Chinese and international shipping companies, port enterprises and think tanks, among other bodies, have joined the Silk Road Maritime association.
A marine environment forecast and support system that focuses on areas along the Maritime Silk Road offers services to more than 100 cities in participating countries.
The Air Silk Road has made notable progress. The aviation route network between participating countries is expanding rapidly, and the level of air connectivity is steadily improving.
China has signed bilateral air transport agreements with 104 BRI partner countries and opened direct flights with 57 partner countries to facilitate cross-border transport.
Chinese enterprises are active participants in civil aviation infrastructure cooperation with partner countries including Pakistan, Nepal and Togo, helping to develop the local civil aviation industry.
A BRI cooperation platform proposed by the Civil Aviation Administration of China was established in August 2020, improving mechanisms and platforms of civil aviation exchanges and cooperation among participating countries.
During the Covid-19 pandemic, a direct line of the Air Silk Road linking Zhengzhou in Henan Province and Luxemburg did not suspend its air or freighting services, and transported a large amount of supplies. It served as an air lifeline between China and Europe, and contributed to keeping international industrial and supply chains stable.
International inter-modality transport channels continue to enjoy stable development. These channels include the China-Europe Railway Express, the China-Europe Land-Sea Express Line, the New International Land-Sea Trade Corridor, and the Lianyungang-Khorgos New Eurasian Land-Sea Expressway.
The China-Europe Railway Express has now reached more than 200 cities in 25 European countries, comprising 86 routes passing through the main regions of the Eurasian hinterland at a speed of 120 km per hour. Its logistics distribution network covers the entire Eurasian continent. By the end of June 2023, the cumulative volume of the China-Europe Railway Express had exceeded 74,000 trips, transporting nearly 7 million TEUs and over 50,000 types of goods in 53 categories such as automobiles, mechanical equipment, and electronic products, to a total value of more than US$300 billion.
The China-Europe Land-Sea Express Line has emerged from scratch to become the third trade channel between China and Europe, after traditional sea routes and the China-Europe Railway Express. In 2022, more than 180,000 TEUs were transported through this line, with rail trips exceeding 2,600.
The routes of rail-sea freight trains of the New International Land-sea Trade Corridor cover 18 provinces and equivalent administrative units, in central and western China, transporting goods to 300-plus ports in more than 100 countries.
Facilitating trade and investment is a major task in building the Belt and Road. The participating countries have worked hard to promote trade and investment liberalization and facilitation, remove investment and trade barriers, and improve the business environment within the region and in all related countries. Efforts have been made to build free trade zones, broaden trading areas, improve trade structure, expand areas of mutual investment and industrial cooperation, establish a more balanced, equal and sustainable trading system, and develop mutually beneficial economic and trade relations, so as to make the “pie” of cooperation bigger.
Trade and investment are expanding steadily. From 2013 to 2022, the cumulative value of imports and exports between China and BRI partner countries reached US$19.1 trillion, with an average annual growth rate of 6.4 percent. The cumulative two-way investment between China and partner countries reached US$380 billion, including US$240 billion from China. The value of newly signed construction contracts with partner countries reached US$2 trillion, and the actual turnover of Chinese contractors reached US$1.3 trillion. In 2022, the value of imports and exports between China and partner countries reached nearly US$2.9 trillion, accounting for 45.4 percent of China’s total foreign trade over the same period, representing an increase of 6.2 percentage points compared with 2013; the total value of imports and exports of Chinese private enterprises to partner countries exceeded US$1.5 trillion, accounting for 53.7 percent of the trade between China and these countries over the same period.
Trade and investment liberalization and facilitation is improving. BRI participating countries continue to uphold multilateralism and free trade, working hard to create a sound institutional environment for closer economic and trade relations. Positive progress has been made in the alignment of working systems, coordination of technical standards, mutual recognition of inspection results, and online verification of electronic certificates.
By the end of August 2023, more than 80 countries and international organizations had subscribed to the Initiative on Promoting Unimpeded Trade Cooperation Along the Belt and Road, proposed by China. China had signed 21 free trade agreements with 28 countries and regions. On January 1, 2022, the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) agreement entered into force, creating the world’s largest free trade zone in terms of population size and trade volume. The RCEP and the BRI overlap and complement each other in terms of participating countries and regions, as well as areas and contents of cooperation, forming a new dynamic of economic and trade cooperation in Asia.
China also works actively towards joining the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership and the Digital Economy Partnership Agreement.
China has signed bilateral investment agreements with 135 countries and regions, and conventions for the avoidance of double taxation (including arrangements and agreements) with 112 countries and regions. It has achieved Authorized Economic Operator mutual recognition with 35 partner countries, and has signed third-party market cooperation documents with 14 countries.
China has established a “single-window” cooperation mechanism with Singapore, Pakistan, Mongolia, Iran and other partner countries, and signed cooperation documents on customs inspection and quarantine, effectively improving the efficiency of customs clearance at border ports.
Trade and investment platforms are playing a growing role. China International Import Expo (CIIE) is the world’s first import-themed national-level expo and has been held for the past five years. It has resulted in a cumulative intended turnover of nearly US$350 billion, and about 2,000 launches of new products. With diverse participants from many countries and regions, the CIIE has become a global platform for international procurement, investment promotion, cultural exchanges, and open cooperation.
The influence of key exhibitions continues to expand; these include China Import and Export Fair (Canton Fair), China International Fair for Trade in Services, China International Fair for Investment and Trade, China International Consumer Products Expo, Global Digital Trade Expo, China-Africa Economic and Trade Expo, China-Arab States Expo, China-Russia Expo, China-CEEC Expo & International Consumer Goods Fair, China-ASEAN Expo, and China-Eurasia Expo. All of these have provided a strong boost to trade and investment cooperation among participating countries.
The Hong Kong SAR has held the Belt and Road Summit eight times, and the Macao SAR has held the International Infrastructure Investment and Construction Forum 14 times, which have played an important role in advancing economic, trade and investment cooperation along the Belt and Road.
Industrial cooperation is deepening. BRI participating countries have worked hard to foster a paradigm of cooperation based on coordinated development, mutual benefit, and win-win outcomes, which has given a strong boost to upgrading industrial structures and optimizing industrial chains in the countries involved.
The participating countries have jointly promoted cooperation on industrial capacity, expanded cooperation in traditional industries including steel, non-ferrous metals, building materials, automobiles, engineering machinery, resources and energy, and agriculture, explored cooperation in emerging industries such as the digital economy, new energy vehicles, nuclear energy and technology, and 5G, and carried out tri-party and multiparty market cooperation, thus advancing mutual complementarity and providing mutual benefits to all parties.
By the end of June 2023, China had signed agreements on industrial capacity cooperation with more than 40 countries. China Mining Conference & Exhibition and China-ASEAN Mining Cooperation Forum & Exhibition serve as important platforms for participating countries to conduct mining capacity cooperation.
The Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) Demonstration Base for Agricultural Technology Exchange and Training has supported advances in agricultural science and technology under the BRI, and promoted economic and trade cooperation in agriculture among participating countries.
Jointly constructed by China and Pakistan, the K2 and K3 units of the Karachi Nuclear Power Plant have been completed and are in operation, utilizing China’s Hualong One nuclear technology.
The Ulba Fuel Assembly Plant, a successful joint venture between China and Kazakhstan, is now operational.
The China-ASEAN Forum on Peaceful Uses of Nuclear Technology has served as a bridge to establish connectivity, enabling BRI participating countries to cooperate on nuclear technology and promote growth and people’s wellbeing.
More than 70 overseas industrial parks have been built by Chinese enterprises together with governments and enterprises in partner countries. The China-Malaysia and China-Indonesia “Two Countries, Twin Parks” projects, the China-Belarus Great Stone Industrial Park, the China-UAE Industrial Capacity Cooperation Demonstration Zone, and the China-Egypt TEDA Suez Economic and Trade Cooperation Zone are making steady progress.
Financial integration is an important pillar of BRI cooperation. Participating countries and relevant institutions have carried out multiple forms of financial cooperation, created new models, expanded the channels, diversified the parties involved, and improved the mechanisms for investment and financing. They have promoted policy-based finance, development finance, commercial finance, and cooperative finance to support BRI cooperation, and worked to build a long-term, stable and sustainable investment and financing system that keeps risk under control.
The financial cooperation mechanisms are maturing. China Development Bank (CDB) has promoted the establishment of multilateral financial cooperation mechanisms such as China-Central and Eastern Europe Interbank Consortium, the China-Arab Countries Interbank Association, China-ASEAN Interbank Association, the ASEAN Plus Three Interbank Cooperation mechanism, China-Africa Interbank Association, and the Association of China-LAC Development Financial Institutions. The Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC) has promoted the Belt and Road Interbank Regular Cooperation (BRBR) mechanism.
As of the end of June 2023, a total of 13 Chinese-funded banks had established 145 first-tier offices and branches in 50 BRI partner countries; some 17.7 million businesses in 131 partner countries had opened UnionPay services, and 74 partner countries had opened UnionPay mobile payment services. The Belt and Road Innovation and Development Center, the Research Center for Belt and Road Financial and Economic Development, and the China-IMF Capacity Development Center have been established.
China has signed bilateral currency swap agreements with 20 partner countries and established renminbi (RMB) clearing arrangements in 17 partner countries. The number of participants, business volume, and influence of the RMB cross-border payment system have gradually increased, effectively facilitating trade and investment.
Financial regulation cooperation and exchanges have continued to move forward. China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (now National Administration of Financial Regulation), China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC), and regulatory agencies from multiple other countries have signed memorandums of understanding (MoUs) for regulatory cooperation, facilitating the establishment of regional regulatory coordination mechanisms, promoting efficient allocation of funds, strengthening risk control, and creating sound investment conditions for various financial institutions and investment entities.
The channels and platforms for investment and financing are constantly expanding. China has funded the establishment of the Silk Road Fund (SRF) and established the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) with other participating countries. The SRF specifically serves BRI cooperation. By the end of June 2023, the fund had signed agreements on 75 projects with committed investment of about US$22 billion; the number of AIIB members had reached 106, and the bank had approved 227 projects with a total investment of US$43.6 billion. The projects involve transport, energy, public health and other fields, providing investment and financing support for infrastructure connectivity and sustainable economic and social development.
China has actively participated in various existing financing arrangements. It has signed memorandums of cooperation with international financial institutions such as the World Bank and the Asian Development Bank, worked with international financial institutions to establish a multilateral development financing cooperation center, strengthened third-party market cooperation in investment and financing with the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, and carried out joint financing with the International Finance Corporation, the African Development Bank and others. These moves have effectively mobilized market capital.
China has initiated the establishment of international economic cooperation funds such as the China-Eurasian Economic Cooperation Fund, the China-LAC Cooperation Fund, the China-Central and Eastern Europe Investment Cooperation Fund, the China-ASEAN Investment Cooperation Fund, the China-LAC Industrial Cooperation Investment Fund, and the China-Africa Fund for Industrial Cooperation. These have effectively expanded investment and financing channels for partner countries.
The CDB and the Export-Import Bank of China (China Eximbank) have each set up special loans for the BRI to pool resources to increase financing support for BRI cooperation. By the end of 2022, the CDB has provided direct high-quality financial services for more than 1,300 BRI projects, playing a leading role in guiding development finance, and pooling all kinds of domestic and foreign funds for BRI cooperation. The balance of loans of China Eximbank for BRI projects reached RMB2.2 trillion, covering 130-plus participating countries and driving more than US$400 billion of investment and more than US$2 trillion of trade. China Export & Credit Insurance Corporation has fully applied export credit insurance and actively provided comprehensive guarantees for building the Belt and Road.
Innovative investment and financing methods are steadily being explored. Various models such as funds and bonds have been developed, and BRI financial cooperation is improving.
China’s securities industry has set up a number of BRI-themed funds and indexes. In December 2015, the CSRC officially launched a pilot project for overseas institutions to issue RMB-denominated bonds (panda bonds) in China’s exchange-traded bond market. By the end of June 2023, overseas issuers in total had issued 99 panda bonds in China’s exchange-traded bond market, with a total value of RMB152.54 billion; 46 BRI-themed bonds had been issued, with a total value of RMB52.72 billion.
Green finance is steadily developing. In May 2019, the ICBC issued the first green BRBR bond that conformed to both international and domestic green bond standards. By the end of 2022, more than 40 large global institutions had signed the Green Investment Principles for the Belt and Road. In June 2023, China Eximbank issued financial bonds for promoting international cooperation in building the Belt and Road and supporting infrastructure construction of partner countries. China’s domestic stock and futures exchanges have steadily promoted practical cooperation in equity, products, technology and other fields with the exchanges in partner countries, and actively supported the development of exchanges participating in or holding shares in BRI projects, such as the Astana International Exchange in Kazakhstan, the Pakistan Stock Exchange, and the Dhaka Stock Exchange in Bangladesh.
Debt sustainability has continued to improve. Based on the principle of equal participation and benefit and risk sharing, China and 28 countries approved the Guiding Principles on Financing the Development of the Belt and Road, encouraging the governments, financial institutions and enterprises of participating countries to attach importance to debt sustainability and improve their debt management capability. Drawing on the debt sustainability framework of low-income countries endorsed by the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank, China has developed tools based on the actual conditions of participating countries, and issued the Debt Sustainability Framework for Participating Countries of the Belt and Road Initiative. All parties are encouraged to use it on a voluntary basis.
To avoid causing debt risk and financial burden to the countries where BRI projects are located, China has prioritized economic and social benefits and provided loans for project construction based on local needs and conditions. The key areas of investment are infrastructure projects designed to increase connectivity, and projects for public wellbeing urgently needed in participating countries. These have brought effective investment, increased high-quality assets, and boosted development momentum.
Many think tank experts and international institutions have pointed out that almost all the BRI projects are initiated by the host countries with the goals of growing their economies and improving their people’s lives. In the process, the logic of economics has taken precedence over geopolitics.
People-to-people ties are the social foundations of BRI cooperation. The participating countries have passed on and carried forward the spirit of friendly cooperation of the ancient Silk Road, cooperated on exchanges in culture, tourism, education, think tank and the media, and promoted mutual learning among civilizations and cultural integration and innovation. A model of people-to-people exchanges characterized by dynamic interactions and diversity has underpinned public support for furthering the initiative.
Cooperation on culture and tourism is rich and colorful. By the end of June 2023, China had signed cultural and tourism cooperation documents with 144 BRI partner countries.
China has created cooperation platforms together with participating countries, including the Silk Road International League of Theaters, the Silk Road International Museum Alliance, the Network of Silk Road Arts Festivals, the Silk Road International Library Alliance, and the Silk Road International Alliance of Art Museums and Galleries. These platforms have a total of 562 members, including 326 cultural institutions from 72 partner countries.
China is steadily expanding international cultural exchanges. China has launched the Cultural Silk Road program, and organized signature events such as the Happy Chinese New Year celebrations, the Nihao China tourism promotions, and the Silk Road: Artists’ Rendezvous art exhibition. It has worked with Brunei, Cambodia, Greece, Italy, Malaysia, Russia and ASEAN to co-host cultural and tourism activities at designated years. China and BRI partner countries have hosted events in a reciprocal manner, ranging from cultural relics exhibitions, film festivals, arts festivals, book fairs and music festivals, and jointly translated and promoted each other’s publishing, radio, film and television programs. They have also implemented the BRI-themed theater arts creation and promotion project, the Belt and Road International Art Project, and the Belt and Road good-neighborliness cultural project, and worked to protect Asian cultural heritage. China has established 46 China cultural centers in 44 countries, of which 32 are partner countries. China has established 20 tourism offices in 18 countries, eight of which are in partner countries.
Educational exchanges and cooperation are extensive and profound. China has released the Education Action Plan for the Belt and Road Initiative to promote international education exchanges and cooperation. By the end of June 2023, China had signed agreements with 45 participating countries on the mutual recognition of higher education degrees.
China has set up the Silk Road Program under the Chinese Government Scholarship scheme. Some of China’s provinces and Hong Kong and Macao SARs, as well as universities and research institutions have also set up scholarships for students from BRI partner countries.
Chinese universities and colleges have opened 313 Confucius Institutes and 315 Confucius Classrooms in 132 partner countries. The “Chinese Bridge” Summer Camp has invited nearly 50,000 young people from more than 100 partner countries to come to China for academic visits, and supported 100,000 Chinese language enthusiasts from 143 partner countries to learn Chinese and experience Chinese culture online.
Chinese universities and colleges have worked with more than 20 counterparts in partner countries from Asia, Africa and Europe to build a number of Luban Workshops – a professional training program dedicated to the sharing of expertise by China’s vocational education institutions.
China and UNESCO have jointly held the International Youth Forum on Creativity and Heritage Along the Silk Roads and relevant activities in seven consecutive years, and established the Silk Roads Youth Research Grant which has funded 24 youth research projects. The Atomic Energy Scholarship of China has funded the education of nearly 200 Master’s and Doctoral students in the field of peaceful use of nuclear energy for 26 BRI partner countries.
Participating countries have capitalized on the demonstration and driving role of the University Alliance and the Alliance of International Science Organizations (ANSO) under the BRI framework, and expanded international exchanges and cooperation in talent training and scientific research.
Media and think tank cooperation has yielded fruitful results. BRI participating countries have held the Media Cooperation Forum on Belt and Road six times, and established the Belt and Road Media Community. The China-Arab States Forum on Radio and Television Cooperation, the Forum on China-Africa Media Cooperation, the China-Cambodia Radio and Television Annual Regular Cooperation Conference, the ASEAN-China Media Cooperation Forum, the Lancang-Mekong Audiovisual Week, and other bilateral and multilateral cooperation mechanisms have been set up. International organizations such as the Asia-Pacific Broadcasting Union and the Arab States Broadcasting Union have become active and important platforms for building consensus among participating countries.
Media outlets in China and partner countries have jointly established the Belt and Road News Network, which launched the Silk Road Global News Awards. By the end of June 2023, the network’s members had increased to 233 media outlets in 107 countries.
Think tank exchanges have become more frequent. The Advisory Council of the Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation was established in 2018. The Silk Road Think Tank Association has recruited 122 partners in Asia, Africa, Europe, and Latin America. Sixteen Chinese and foreign think tanks have established the Belt and Road Studies Network.
People-to-people exchanges are constantly expanding. Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) continue to strengthen cooperation with the goals of benefiting the people, improving their lives, and connecting their hearts. At the people-to-people ties sub-forum of the Second Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation, Chinese and foreign NGOs, including China NGO Network for International Exchanges, combined to launch the Silk Road Community Building Initiative, encouraging Chinese and foreign NGOs to establish nearly 600 cooperative partnership pairings and carry out more than 300 cooperation projects for improving people’s lives. Of these, some brand projects have achieved a wide impact, including the Shenzhen-Lancang-Mekong Cooperation to benefit the people in the Lancang-Mekong region with Shenzhen’s advanced products and technology, the Panda Pack Project to provide primary school students with learning supplies, and the Brightness Journey program to provide free cataract surgery to those in need.
Cities from 60-plus BRI partner countries have formed more than 1,000 pairs of friendly cities with their Chinese counterparts. A total of 352 NGOs from 72 countries and regions have formed a Silk Road NGO Cooperation Network, carrying out over 500 projects and various other activities, and becoming an important platform for exchanges and cooperation between NGOs in participating countries.
Leveraging their respective strengths, participating countries have continued to expand BRI cooperation into new fields and created innovative cooperation models, achieving great progress in building a healthy, green, innovative and digital Silk Road and further broadening the space for international cooperation.
Notable achievements have been made in health cooperation. To establish closer partnerships in health cooperation, participating countries are working hard to build a Health Silk Road and a global community of health for all. By the end of June 2023, China had signed an MoU with the WHO on health cooperation in BRI partner countries, inked health cooperation agreements with more than 160 countries and international organizations, and initiated or participated in nine international and regional health cooperation mechanisms, including China-Africa Health Cooperation, China-Arab States Health Cooperation, and China-ASEAN Health Cooperation.
Relying on mechanisms and platforms such as the Belt & Road Health Professionals Development Alliance, the Belt & Road Hospital Cooperation Alliance, the Belt & Road Health Policy Research Network, and the China-ASEAN Human Resources Training Program of Health Silk Road (2020-2022), China has helped BRI partner countries to train tens of thousands of professionals in health management, public health and medical research. It has also dispatched medical teams to 58 partner countries, and provided free treatment for nearly 10,000 cataract patients in more than 30 partner countries through the Brightness Journey program. In addition, China has sent several rounds of medical aid to island states of the South Pacific, and carried out international medical cooperation with neighboring countries, including countries of the Greater Mekong Subregion, Central Asian countries, and Mongolia.
After the outbreak of Covid-19, China provided assistance to more than 120 BRI partner countries to combat the pandemic, and sent 38 expert medical teams to 34 countries. It started the Initiative for Belt and Road Partnership on Covid-19 Vaccines Cooperation together with 31 countries, delivered more than 2 billion doses of vaccines to partner countries, and conducted joint vaccine production with more than 20 countries, improving vaccine affordability and accessibility in developing countries.
In addition, China has signed documents on traditional medicine cooperation with 14 BRI partner countries; eight partner countries have taken measures to support the development of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) within the framework of their respective legal systems; 30 overseas TCM centers have been built; and 100-plus TCM drugs have been registered and marketed in partner countries.
Remarkable progress has been achieved in green and low-carbon development. China is working together with partner countries and international organizations to build a cooperation mechanism for green and low-carbon development under the BRI framework, promote green development, and address climate change.
China has issued documents such as the Guidance on Promoting Green Belt and Road and the Guidelines on Jointly Promoting Green Development of the Belt and Road, and set itself the ambitious goal of forming a basic framework of green development through BRI cooperation by 2030. China has also signed an MoU with the United Nations Environment Programme on building a green Belt and Road for 2017-2022, reached environmental cooperation agreements with more than 30 countries and international organizations, launched the Initiative for Belt and Road Partnership on Green Development together with 31 countries, formed the Belt and Road Initiative International Green Development Coalition with more than 150 partners from 40-plus countries, and established the Belt and Road Energy Partnership with 32 countries.
China has pledged to stop building new coal-fired power stations overseas, and to actively build green finance platforms and international cooperation mechanisms. It stands ready to cooperate with partner countries on research into biodiversity conservation, safeguarding the eco-environmental security of the Maritime Silk Road, building the Belt and Road Big Data Service Platform on Ecological and Environmental Protection and the Belt and Road Environmental Technology Exchange and Transfer Center, and implementing the Green Silk Road Envoys Program.
China is actively promoting the Belt and Road South-South Cooperation Initiative on Climate Change. It has signed 47 South-South MoUs on climate change with 39 partner countries, built low-carbon demonstration zones with Laos, Cambodia, and Seychelles, carried out more than 70 climate change mitigation and adaptation projects with 30-plus developing countries, and trained more than 3,000 environment management personnel and experts from more than 120 countries.
In May 2023, China Eximbank, together with a dozen financial institutions including China Development Bank, and China Export & Credit Insurance Corporation, released the Initiative for Supporting Belt and Road Energy Transition with Green Finance, calling on all parties involved to strengthen support for green and low-carbon energy transition in BRI participating countries.
Cooperation in scientific and technological innovation is gathering speed. BRI participating countries are strengthening cooperation on innovation, facilitating technology transfer and knowledge sharing, optimizing the innovation-enabling environment, and pooling innovation resources. They are also building up their capacity for scientific and technological innovation through cooperation in major projects and talent training.
In October 2016, China released the Special Plan on Advancing Belt and Road Cooperation in Scientific and Technological Innovation. In May 2017, the Action Plan on Belt and Road Cooperation in Scientific and Technological Innovation was implemented, to increase the capacity for innovation in BRI participating countries through pragmatic measures such as joint research, technology transfer, exchanges in science, technology and culture, and cooperation between high-tech industrial parks.
By the end of June 2023, China had signed intergovernmental agreements on scientific and technological cooperation with more than 80 BRI partner countries, and 58 members had joined the ANSO. Since 2013, China has hosted more than 10,000 young scientists from partner countries in carrying out short-term research and exchanges in China, and trained more than 16,000 technicians and management professionals for partner countries; China has established nine cross-border technology transfer platforms targeting ASEAN, South Asia, Arab states, Africa, Latin America, and other regions; China has assisted 22 African countries to build 23 agricultural technology demonstration centers, and set up 50-plus BRI joint laboratories in areas such as agriculture, new energy, and health.
China has signed an agreement with the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) on strengthening BRI cooperation on intellectual property and additional agreements on subsequent revision and prolongation of the said agreement. China and the WIPO have jointly hosted twice the High-level Conference on Intellectual Property for Countries Along the Belt and Road, and released a joint initiative and a joint statement on strengthening cooperation on intellectual property. To date, China has established intellectual property cooperation relationships with more than 50 partner countries and international organizations, whose goal is to create an innovation and business environment in which the value of knowledge is duly respected.
Digital silk road cooperation presents numerous highlights. BRI participating countries have joined to create an open, fair, equitable and non-discriminatory environment for digital development by strengthening facilitation of and cooperation on rules and standards and promoting regional policy coordination.
By the end of 2022, China had signed MoUs on building the Digital Silk Road with 17 countries, MoUs on e-commerce cooperation with 30 countries, and MOUs on closer investment cooperation in the digital economy with 18 countries and regions. It has proposed and worked to launch the Global Initiative on Data Security, the Belt and Road Digital Economy International Cooperation Initiative, the initiative for building the ASEAN-China Partnership on Digital Economy Cooperation, the China-League of Arab States Cooperation Initiative on Data Security, the China + Central Asia Data Security Cooperation Initiative, and the BRICS Digital Economy Partnership Framework, among others. It also took lead in formulating the Framework of Standards on Cross-border E-commerce.
China is active in strengthening digital infrastructure connectivity and is stepping up work on digital corridors. Several international submarine cables have made positive progress, and 130 cross-border terrestrial cable systems have been built.
China has built many 5G base stations, data centers, cloud computing centers and smart cities, and promoted digital upgrading and transformation of traditional infrastructure such as ports, railways, highways, energy networks and water conservancy facilities.
A number of key projects such as the China-ASEAN Information Harbor, and the digital platform of China-Europe Railway Express and
the China-Arab Online Silk Road is making good progress, and the DBAR Big Earth Data Platform has realized multilingual data sharing.
Thriving new business models of international trade, represented by cross-border e-commerce and overseas warehouses, are providing better services and more choice to global consumers, and promoting global trade innovations. Silk Road E-commerce is an important means by which China can capitalize on its strengths in e-commerce technology application, model innovation and market size, expand economic and trade cooperation, and share the opportunities of digital development with BRI participants.By the end of September 2023, China had established bilateral mechanisms of e-commerce cooperation with 30 countries on five continents; multilateral mechanisms had been built under the China-CEEC and China-Central Asia frameworks.
Activities such as the Silk Road E-commerce Platform of the Brand and Quality Online Shopping Festival and the Quality African Products Online Shopping Festival have yielded substantial results, and virtual country pavilions help partner countries to export their high-quality specialty products to the Chinese market.The innovative Cloud Classroom program has provided livestreamed training sessions for more than 80 participating countries to reinforce their digital literacy.Through consistently enriching the content and elevating the level of cooperation, Silk Road E-commerce has become a new platform for bilateral and multilateral economic and trade cooperation and a new strength in high-quality BRI cooperation.
The construction of the Belt and Road Initiative Space Information Corridor has been a resounding success. China has built teleports connecting South Asia, Africa, Europe, and the Americas. The data from remote sensing satellites under the China-Brazil Earth Resources Satellite (CBERS) program is widely used in multiple countries and fields. The BeiDou navigation satellite system (BDS-3) provides comprehensive services for China-Europe Railway Express, and in maritime transport and other fields.
China and a number of BRI partner countries and regions have combined to develop and launch communication or remote sensing satellites, and constructed satellite ground stations and other space infrastructure. Through the Regional Centre for Space Science and Technology Education in Asia and the Pacific (China) affiliated to the United Nations, China has trained a large number of space professionals for partner countries. Together with other countries and regions, China has built the China-GCC Joint Center for Lunar and Deep Space Exploration, the China-UAE Space Debris Joint Monitoring Center, the Lancang-Mekong Cooperation Center for Earth Observation Data, the China-ASEAN Satellite Remote Sensing Application Center, and the China-Africa Cooperation Center on Satellite Remote Sensing Application. The CNSA-GEO platform, the Belt and Road Analysis and Early Warning Platform for Typical Meteorological Disasters, and the Natural Resources Satellite Remote Sensing Cloud Service Platform now serve many partner countries.
1 – Injecting Positive Energy into World Peace and Development
Over the past decade, BRI cooperation has witnessed remarkable results. It has opened up new space for world economic growth, built a new platform for international trade and investment, reinforced the development capacity of relevant countries and improved people’s lives, sought ways to improve the global governance system, and brought greater certainty and stability to a world fraught with turbulence and change. The BRI has boosted China’s development and benefited the rest of the world.
2 – Bringing tangible benefits to participating countries
Development is an eternal theme for humanity. The BRI has focused on the fundamental issue of development, addressing the weaker links and bottlenecks that hinder development, building new engines for economic development, and creating a new development environment and space for participating countries. This has strengthened their confidence and their capacity for development, and improved their people’s lives. The initiative has contributed to addressing global development imbalance and advancing modernization in all countries.
Boosting development in participating countries. Over the last 10 years, the BRI has addressed the major bottlenecks restricting connectivity and economic growth in most of the developing countries. A large number of infrastructure projects have been built, with significant progress for participating countries in the construction of railways, highways, pipelines, shipping, energy, communications and other basic public service facilities. This has improved local living and working conditions and the development environment, and boosted their capacity for independent economic development.
Some engineering projects with a long construction cycle are like seeds sown in a field, gradually generating comprehensive benefits for the long term. Connectivity in infrastructure has effectively reduced the cost for countries to participate in international trade, increased their access to the global economy, and stimulated the potential and impetus for their development. Research by the Asian Development Bank shows that lowering a landlocked country’s trade costs by 10 percent through improvement in infrastructure could increase its exports by 20 percent.
Industrial capacity cooperation has promoted industrialization, digitization, informatization, and the structural upgrading of industries in participating countries. It has helped them to form competitive industrial systems and expand the breadth and depth of their participation in the international division of labor and cooperation, creating more opportunities and greater space for development.
China has actively conducted international cooperation in emergency management. It has sent rescue teams to Nepal, Mozambique, Türkiye and other countries to carry out humanitarian operations following earthquakes and floods, and provided emergency supplies and technical support to Tonga and Madagascar, among other countries.
Building poverty reduction capacity in participating countries. Developing countries still face the challenge of problems related to food. China has taken an active part in global food and agriculture governance. It has released the Vision and Action on Jointly Promoting Agricultural Cooperation Along the Belt and Road with partner countries, and signed more than 100 agricultural and fishery cooperation documents with almost 90 partner countries and international organizations. Its trade in agricultural products with BRI partners has reached US$139.4 billion. China has sent more than 2,000 agricultural experts and technicians to over 70 countries and regions, and introduced more than 1,500 agricultural technologies such as Juncao and hybrid rice to many of these countries. It has helped with rural poverty reduction in Asia, Africa, the South Pacific, Latin America, and the Caribbean, developing modern agriculture and helping to increase farmers’ incomes.
Boosting employment is an important element of poverty reduction. In the process of BRI cooperation, China has helped to construct industrial parks with participating countries and provided guidance for Chinese enterprises to create jobs for local residents through high-level industrial cooperation. The jobs provided to locals have helped to lift their families out of poverty. A McKinsey survey revealed that Chinese firms in Africa recruited 89 percent of their employees locally, contributing to local employment in an effective way.
The World Bank has estimated that by 2030, BRI-related investments could lift 7.6 million out of extreme poverty and 32 million out of moderate poverty.
China’s Juncao technology makes comprehensive and efficient utilization of three major agricultural resources – light, heat and water. It makes circular production based on plants, animals, and fungi possible, combines economic, social and environmental benefits, and supports food, energy, and eco-environmental security.Juncao technology was first launched as an official assistance project in 2001, in Papua New Guinea. Over the last two decades, China has hosted more than 270 international training courses on Juncao technology, for more than 10,000 trainees from 106 countries. It has also established Juncao technology demonstration centers or bases in 13 countries in Asia, Africa, Latin America, and the South Pacific region. Today, Juncao technology is being applied in more than 100 countries, creating hundreds of thousands of green jobs for local youth and women. A former cabinet minister of Papua New Guinea named his daughter Juncao. The people of Lesotho have produced folk songs in praise of Juncao which are still popular today. In 2017, Juncao technology was listed as a key project of the China-UN Peace and Development Fund, contributing more Chinese know-how to the cause of international poverty reduction.
Delivering notable results in projects that improve people’s lives. Chinese firms have repaired and maintained bridges to make it easier for local residents to travel. They have drilled wells to meet local villagers’ needs for drinking water. They have installed street lamps for pedestrians to see clearly on their way home at night. Many such seemingly small projects have solved urgent problems for local people and improved their daily lives. They have brought tangible benefits to the people of participating countries, and increased their sense of gain, fulfillment and security.
Over the last 10 years, Chinese firms have launched more than 300 poverty alleviation, health care and rehabilitation, and Happy Home projects in participating countries. They have helped with the construction of the headquarters of Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention and the China-Pakistan Fraternity Emergency Care Center in Gwadar, Pakistan. They have also helped Cameroon, Ethiopia, Djibouti and other countries to provide clean drinking water for the local people.
n January 2020, China launched the Lancang-Mekong Sweet Spring Project, a project demonstrating rural water supply safety technology in the Lancang-Mekong region. Water supply facilities were built in rural areas of Cambodia, Laos, and Myanmar, markedly improving local water supply capacity and safety. Through this project, China has helped to improve the lives of local people and played an active role in helping the Lancang-Mekong region to access clean water and sanitation, one of the United Nations 2030 Sustainable Development Goals.As of December 2022, 62 demonstration sites had been built in the project area, ensuring safe drinking water for more than 7,000 local people. China had also trained over 400 personnel from the region in rural water supply management and project management.
The Silk Road Community Building Initiative has promoted projects in more than 20 areas, including poverty alleviation and disaster relief, humanitarian assistance, environmental protection, and women’s exchanges and cooperation. Related activities have had an extensive impact.
Against a rising tide of de-globalization, the BRI is committed to global connectivity and interconnected development. It has further opened up the main arteries of economic globalization, facilitated the flow of information, capital, technology, product, industry and people, and promoted closer and broader international cooperation. By expanding economic globalization and distributing its benefits fairly, the BRI aims to promote global development that is balanced, coordinated, inclusive and shared by all, and that brings win-win cooperation and common prosperity.
Boosting the momentum for global development. The BRI has connected the vibrant East Asia economic circle at one end, the developed European economic circle at the other, and the countries in between with huge potential for economic development, and fostered closer economic cooperation with African and Latin American countries. It has formed a new global development dynamic in which the Eurasian continent is fully connected with the Pacific, Indian and Atlantic oceans, and the land is integrated with the sea. It has expanded the scope and coverage of the international division of labor in a broader economic and geographical space, and enlarged the global market, which ultimately promoted new global economic growth.
At the same time, through infrastructure connectivity, the BRI has proved a catalyst to international investment and boosted global interest in and enthusiasm for investment in infrastructure, which provides economic growth and rapid development in participating countries. These efforts have effectively addressed the shortage of international public goods and provided sustained impetus for world economic growth.
Encouraging deeper regional economic cooperation. In strengthening infrastructure connectivity, the BRI promotes connectivity between countries in many directions and various fields. The BRI turns dots into lines and lines into fields, gradually amplifying the radiation effect of development. It encourages countries to coordinate economic policies, systems and mechanisms, and innovate cooperation models, conduct broader, deeper and closer regional cooperation, and jointly create an open, inclusive and balanced regional economic cooperation architecture that benefits all. It has facilitated a freer and more orderly flow of economic factors, more efficient allocation of resources, and deeper integration of markets, and upgraded economic and trade connectivity and vitality between countries and regions, and the overall position of participating countries in global industry chains, supply chains, and value chains.
Participating countries have made full use of their own factor endowments to integrate, coordinate, and upgrade their industry chains, promote industrial complementarity, and improve the efficiency of division of labor. They have broken down trade barriers and market monopolies, unleashed internal and cross-border consumption potential, and expanded the scale of regional markets. Through technology transfer and cooperation in industrial cooperation, they have established technology interaction and interdependence, strengthened capacity for innovation, and promoted leapfrog development.
Promoting global trade. The BRI supports the liberalization and facilitation of trade and investment by building transport and information infrastructure in a planned and progressive manner. It has eliminated internal, transnational, and inter-regional transport bottlenecks and barriers to trade and investment cooperation, made cross-border logistics and foreign trade easier and more convenient, and increased the efficiency of domestic and international cooperation. It has built up an all-round, multi-level and complex network of unimpeded trade, creating a new dynamic and greatly facilitating global trade.
At the same time, the BRI has made participating countries more attractive to quality global capital, and contributed to rising direct cross-border investment in these countries. In 2022, cross-border direct investment inflows in Southeast Asia accounted for 17.2 percent of the global total, 9 percentage points higher than in 2013. The inflow of FDI into Kazakhstan grew by a historical high of 83 percent year on year.
World Bank study – “Belt and Road Economics: Opportunities and Risks of Transport Corridors” – estimates that prior to the BRI, the six corridor economies under trade with each other and the rest of the world by 30 percent on average and they fall short of their absorptive potential of FDI by 70 percent. Transport infrastructure projects under the BRI would reduce trade costs for the world by 1.8 percent, and reduce trade costs along the China-Central Asia-West Asia economic corridor by 10 percent. This has greatly facilitated global trade and boosted economic growth. The study projects that trade growth would range between 2.8 and 9.7 percent for corridor economies and between 1.7 and 6.2 percent worldwide, and global real income is expected to increase by 0.7 to 2.9 percent.
Maintaining the stability of global supply chains. An efficient and interconnected international transport corridor established under the BRI framework plays an important role in maintaining the stability and smooth flow of global supply chains.
During the Covid-19 outbreak, ports and logistics companies canceled or reduced services for shipping and freight transport, which had dealt a hard blow to those global supply chains which were highly dependent on shipping.
The China-Laos Railway is an electrified railway directly connecting Kunming City of China with Vientiane City of Laos. It is the first transnational railway built under the BRI, funded mainly by Chinese investment, operated jointly by the two sides, and connected directly with China’s railway network. The 1,035-km-long railway officially opened for business on December 3, 2021. On April 13, 2023, the China-Laos Railway started cross-border passenger services, with bullet trains running directly in both directions between Kunming and Vientiane.As an important part of the central section of the pan-Asia railway network, the China-Laos Railway has helped Laos to realize its long-cherished dream of becoming a land-linked country from a landlocked one. It has promoted transport, investment, logistics and tourism, and injected new impetus into the economic development of Laos and areas along the line. By August 31, 2023, the railway had recorded a total of 20.79 million passenger trips and carried 25.22 million tonnes of cargo. It has become a safe and efficient international passageway connecting Laos with its neighboring countries and regions and generating mutual benefits.The China-Laos Railway is a project that wins the heart of the people and an example of clean management. The leaders of China and Laos reached an important agreement on making the China-Laos Railway a clean project. The discipline inspection and supervision departments of the two countries established a government-level supervision and coordination mechanism, and the enterprises involved in construction had taken incorruptibility as a top priority from project design and deployment through to implementation and review. Effective systems were in place to enforce this principle throughout construction, and new methods of cooperation to fight corruption were tested. Through the efforts of both parties, the China-Laos Railway has become a road of friendship, integrity and happiness.According to a World Bank study – “From Landlocked to Land-Linked: Unlocking the Potential of Lao-China Rail Connectivity” – the China-Laos Railway could raise Laos’ aggregate income by up to 21 percent over the long term. The transit trade through Laos along the line is estimated to reach 3.9 million tonnes per year by 2030, which would include a shift of an estimated 1.5 million tonnes of trade from maritime transport to the railway.
As a key output of BRI cooperation, the China-Europe Railway Express effectively sustained rail connectivity on the Eurasian continent, boosted sea-rail, road-rail, air-rail, and other forms of multimodal transport, and opened up a new transport corridor for the Eurasian continental supply chain. Together with the innovations in customs clearance such as the Customs-Train Operators Partnership for Secure and Expedited Clearance of CR Express Carried Goods (C-TOP), Rapid Customs Clearance for rail service, China made an important contribution to stabilizing the global economy.
Several well-known international logistics associations have stated publicly that the China-Europe Railway Express has provided the world with a reliable logistics solution that can effectively alleviate tensions in the global supply chain and strengthen international logistics.
The deficit in global governance presents a severe challenge to the whole world. The BRI supports genuine multilateralism, and cherishes shared growth through consultation and collaboration in global governance. It advocates dialogue rather than confrontation, removing walls rather than erecting walls, integration rather than decoupling, and inclusiveness rather than exclusion. This is a new paradigm for state-to-state relations that shapes the international order towards greater justice and equality.
Gaining more recognition for the concept of global governance. The BRI’s core principles of “extensive consultation, joint contribution, and shared benefits” have appeared in important documents from international organizations and mechanisms, including the UN and the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation.
The vision of a global community of shared future has developed deep roots. A number of bilateral communities have been built between China and other countries, including Laos and Pakistan. Steady progress has been made in building multilateral communities, including those between China and Africa, the Arab States, Latin America, ASEAN, Central Asia and Pacific Island countries. Practical results have been achieved in building communities in functional areas, including cyber space, maritime cooperation, and health for all.
According to the China’s National Image Global Survey released by the Academy of Contemporary China and World Studies in 2020, the BRI is the Chinese proposal with the highest level of acceptance overseas, with more than 70 percent of respondents recognizing the positive impact of the BRI on individuals, states and global governance. European think tank Bruegel released a paper titled “Global Trends in Countries’ Perceptions of the Belt and Road Initiative” in April 2023, which noted that the BRI is generally positively received in the world, and Central Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, in particular, exhibit strongly positive sentiment towards the BRI.
Improving multilateral governance mechanisms. The BRI upholds the principles of mutual respect and equality, openness, inclusiveness, and win-win results. It enshrines multilateralism by securing international fairness and justice, and protecting the rights and interests of developing countries.
The BRI helps improve the existing multilateral governance mechanisms by firmly upholding the authority and status of the UN, and striving to consolidate and strengthen the stature and effectiveness of global multilateral governance platforms such as the WTO. It actively promotes new multilateral governance mechanisms such as the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, and works with participating parties to promote governance mechanisms in emerging areas such as the deep sea, polar regions, outer space, internet and artificial intelligence.
The BRI has strengthened the position and role of developing countries and emerging economies in the world market system, and increased their discourse power in regional and global economic governance. As a result, the aspirations and concerns of developing countries are increasingly included in the global agenda – a significant improvement in global governance.
Innovating and optimizing global governance rules. Taking into account the differences in the level of economic development, factor endowments, and cultural and religious traditions of relevant parties, the BRI has not preset any rules and standards, nor does it draw ideological lines. Instead, it formulates new rules to solve new problems through full consultation and in-depth exchanges, based on the wishes and needs of the parties involved.
BRI participating countries seek synergy in their strategies, plans, mechanisms, projects, and rules and standards, which helps to optimize the rules for BRI cooperation, and supports the transition from opening up based on the flow of goods and factors of production to opening up based on rules and related institutions. Some rules and standards with strong potential for universal application have been formulated in this process, which has effectively filled in gaps in the global governance system in these areas.
Exchanges and mutual learning among civilizations drive human progress and global peace and development. In contrast to those who persist with black and white thinking, concoct such concepts as the “clash of civilizations” and “superiority of Western civilization”, and provoke large-scale ideological confrontation, the BRI advocates equality, mutual learning, dialogue, and inclusiveness among civilizations, and promotes the shared values of humanity. It has charted a path of exchanges and mutual learning among civilizations for all to prosper individually and collectively, in order to achieve closer ties among peoples and link up the cultures and hearts of all countries.
Improving the mechanisms for people-to-people exchanges. People-to-people exchanges cover a wide range of areas, including politics, culture, the arts, sports, and education. The global influence of various multilateral and bilateral political party exchange mechanisms has increased with the creation of mechanisms such as the CPC and World Political Parties Summit, and the CPC in Dialogue with World Political Parties High-level Meeting. The leading role of high-level inter-party exchanges garners consensus and strengths for stronger people-to-people ties.
Various BRI cooperation mechanisms have emerged, including the Silk Road Think Tank Association, the Belt and Road Initiative Tax Administration Cooperation Mechanism, the ANSO, the Belt and Road Health Professionals Development Alliance, the Silk Road International League of Theaters, and the Silk Road International Museum Alliance. The emergence of such mechanisms has facilitated people-to-people exchanges in diverse forms, promoting mutual understanding, mutual respect, and mutual appreciation among the peoples of all countries.
China, Kyrgyzstan, Iran and other Central and West Asian countries jointly launched the Alliance for Cultural Heritage in Asia – the first international cooperation mechanism regarding Asian cultural heritage – to protect cultural heritage, the tangible carriers of civilization. The projects under the framework of the alliance, for example the protection and restoration of Uzbekistan’s ancient city of Khiva, have been highly commended by UNESCO.
Creating quality brand projects and activities. Several projects and activities have become popular and attracted widespread public participation. Examples include the Silk Road (Dunhuang) International Cultural Expo, the Belt and Road/Great Wall International Folk Culture and Arts Festival, the Silk Road International Arts Festival, the Maritime Silk Road International Arts Festival, the Belt and Road Youth Story, and the Tea Road Cultural Tourism Expo.
Cultural and people-to-people exchange programs have won wide acclaim, including the Silk Road Community Building Initiative, the Kit of Love of medical supplies, Luban Workshops of technical vocational training, the Happy Spring well-drilling project, the Brightness Journey program of free cataract surgeries, the Panda Pack Project of school supplies, the Amity Torch Program of educational assistance, the Belt and Road Tour of Acupuncture-Moxibustion promoting traditional Chinese medicine therapies, and the Confucius Classroom of cultural exchanges.
As these goodwill activities, quality brands, and signature projects continue to emerge, they have become an important means through which all parties can join to strengthen people-to-people ties. This reinforces the sense of identity and belonging of the peoples of all BRI participating countries.
Galvanizing the power of youth. The future of the BRI belongs to the youth. Over the last 10 years, young people in participating countries have engaged proactively in people-to-people exchanges and programs that create a better life. The younger generation has galvanized the tremendous power of youth for strengthening people-to-people bonds and realizing common development.
Lu Ban was an ancient Chinese woodcraft master and inventor. The Luban Workshop, an international exchanges platform for vocational education named after the master, has become a well-known Chinese initiative for introducing Chinese vocational education internationally. Luban Workshops are mainly opened in ASEAN, SCO and African countries.The workshops offer a combination of academic education and vocational training, and share the approach, technology, and standards of Chinese vocational education. The project has built training centers, provided advanced teaching equipment, and sent Chinese teachers and technicians to help train technical personnel for participating countries.
Since the first Luban Workshop opened in Thailand in 2016, Chinese universities and colleges have established dozens of Luban Workshops with more than 20 participating countries in Asia, Africa, and Europe, which offer courses in more than 70 directions, including industrial robots, new energy, and the Internet of Things. The workshops have trained tens of thousands of technical personnel for participating countries, helping more young people to find work. Though small in scale, the workshops respond to people’s desire for a better life, and facilitate the realization of the dream of common development.
The Chinese Youth Global Partnership has received a positive response from all over the world. More than 100 national youth organizations and international organizations have established ties and cooperative relations with China.
Sixteen events of the Belt and Road Youth Story have attracted more than 1,500 young people from participating countries. Focusing on poverty alleviation and reduction, climate change, and pandemic response cooperation, participants shared with the audience their stories and experience in promoting social development and their own development, which vividly demonstrated the right way to view the world from the perspective of appreciation, mutual learning, and sharing.
Other successful activities have also taken place, including the Silk Road Incubator Youth Entrepreneurship Program and the China-Central and Eastern Europe International Forum for Young Innovators, which have become important platforms for the youth of participating countries to strengthen friendly exchanges and cooperation.
Experience over the past 10 years has proved that BRI cooperation responds to the call of the times and benefits the peoples in participating countries. It thus enjoys popular support. It is a path for all participating countries to achieve modernization and a path of hope leading to a bright future. It is resilient and vigorous, and offers broad prospects.
Currently, the world is in a period of turbulence and transformation. Rivalry and competition between major countries is escalating; the geopolitical situation remains tense; global economic recovery is yet to appear over the horizon; cold-war and zero-sum mentalities are resurgent; unilateralism, protectionism and hegemonism are proliferating; populism is making a noticeable resurgence. A new round of technological revolution and industrial transformation has given rise to ever fiercer competition; the deficit in peace, development, security and governance is growing; foreseeable and unforeseeable risks are rising rapidly around the globe. All of this presents unprecedented challenges to humanity.
Certain countries overstretch the concept of national security and seek “decoupling” in the name of “derisking”; they trample international economic and trade order and market rules, and endanger the security and stability of international industrial supply chains; they also impede international humanistic and technological exchanges and cooperation. Their actions raise obstacles to the long-term development of humanity. In a world full of uncertainties and instabilities, all countries should urgently bridge differences through dialogue, oppose rifts with unity, and promote development through cooperation. Against this backdrop, the BRI becomes more meaningful and is an initiative to be welcomed.
In the long term, the trends towards multipolarity and economic globalization, the trend of our times towards peace, development, cooperation and win-win outcomes, and the desire of the people of all countries for a better life will remain unchanged. So will the momentum behind the rise of developing countries as a whole and the status and responsibilities of China as the largest developing country in the world. The BRI faces some difficulties and challenges; however, its future is promising, as long as all countries can manage threats, address challenges, and advance cooperation by considering both their own long-term interests and the overall interests of humanity.
As a large and developing country that meets its responsibilities, China will continue to promote the BRI as its overarching plan and its top-level design for opening up and win-win international cooperation. It will open up on a larger scale, across more areas, and in greater depth. It will steadily expand institutional opening up with regard to rules, regulations, management and standards, and establish new mechanisms for a more open economy. It will achieve high-quality new development through opening up, and provide new opportunities for the world with that development.
China is ready to increase its resource input in global cooperation and do its best to support and help other developing countries to progress faster. It will work to achieve a greater say for emerging economies and developing countries in global governance, and contribute to the common development of all countries. China sincerely welcomes more countries and international organizations to join in cooperation under the BRI, and will support any initiative that can genuinely help developing countries build infrastructure and achieve shared progress, thereby promoting global connectivity and sustainable development.
All countries involved in high-quality BRI cooperation are equal participants, contributors and beneficiaries. China is willing to work with all other parties to strengthen confidence, maintain resolve, and advance BRI cooperation in the spirit of extensive consultation, joint contribution and shared benefits. China hopes that all parties can consolidate the foundations, expand the reach, and optimize the projects of cooperation. Working together, all can create new opportunities, seek new drivers, create new space, and share new fruits of development. All can form closer partnerships in health, connectivity, green development, opening up, inclusiveness, innovation and clean government, and all can thereby participate in fruitful BRI cooperation and provide new and powerful impetus for building a global community of shared future.
The Belt and Road Initiative has given new life to a history of cultural exchanges that dates back more than two millennia, and has inspired more than 150 countries with the zeal to realize new dreams.
In the 10 years that have passed since its launch, cooperation under the BRI framework has brought remarkable and profound change to the world and become a major milestone in the history of humanity.
The BRI is a long-term, transnational and systematic global project of the 21st century. It has succeeded in taking its first step on a long journey. Continuing from this new starting point, the BRI will demonstrate greater creativity and vitality, become more open and inclusive, and generate new opportunities for both China and the rest of the world.
In the future, the BRI will find itself confronted by new difficulties. But as long as all parties involved combine their forces, work together and persevere, we will be able to overcome these problems and raise our extensive consultation, joint contribution, and shared benefits to new heights. Cooperation will thrive, and the BRI can look forward to an even brighter future.
China stands ready to work with other countries to pursue closer and more fruitful cooperation under the BRI framework, implement the Global Development Initiative, the Global Security Initiative and the Global Civilization Initiative, and build an open, inclusive, clean and beautiful world that enjoys lasting peace, universal security and common prosperity. Our goals are to pass on the torch of peace from generation to generation, sustain development, ensure that civilizations flourish, and build a global community of shared future.
后一篇文章 → Please reach saidcherkaoui@triconsultingkyoto.com or by Wechat “edwinleezhiguo” if you need any legal advice on your project finance with Chinese involvement.
10/16/2023搜索
Said El Mansour Cherkaoui December 13, 2022 – updated on October 9, 2023

The preeminence of British banks such as Barings and Rothschild brokerage houses and bankers who traced their profits to the arms trade contingent on the mercantilist trade of Iberian colonialism in Latin America. The shift in the epicenter of world trade had caused continued functional losses to those banking and monetary systems identified in the pretense of imperial domination and conquest.
These changes were promulgated first by the courtesans of the British Crown of Great Britain who promoted the Classical School of economic thoughts which addressed value and money with Adam Smith and David Ricardo which elicited the response of Karl Marx, going through all the changes taking place in Europe giving their inter-bilateral wars and the rise of fierce competition to conquer colonies following the loss of the Northern Hemisphere by the British Crown.
New forms of exchange across the world have been developed in the form of liberal trade and direct transfer of value through the establishment of a direct line of exchange and the transfer of value has been accentuated in Latin America by the abolition of the slave trade and the “newly emancipated slaves” transformed into wage labor. -wages but more masses of unemployed in the cities as in the “Nightmare Fields”.
Territories and countries that remained outside the capitalist mercantile system faced first liberalism and later the direct intervention of colonial companies chartered in London and other European financial centers. Foreign debt has become the spear that crosses the shield of resistant countries to integrate the liberal flow. From India, Central Asia, China to North and South Africa and the Middle East with the “sick man of Europe”, waves and storms invaded them and first accelerated the rise of communist Soviets and into two consecutive world wars and later broke the gold exchange system and paved the way for the first clashes over money and not territories.
International trade has increased over the last hundred years. In 1870, worldwide exports accounted for less than 10% of global output. Today, the value of exported goods is close to 25%. The global trading system has changed in many ways, including:
Many factors have impacted global trade, including:
The Asia Pacific region has been central to this growth, with trade volumes nearly quadrupling in the last twenty years. Factors that drove the globalization of business include:
All this goes back to the time when John Maynard Keynes addressed the question of monetary value during the Bretton Woods and up to the monetarists of Friedman and the Economic School of Chicago and their Avatars as technocrats-military-bureaucrats of ‘Latin America, which was relayed by the Arab boycott and the quadrupling of the price of oil followed by waves of stagflation and we have seen how this to be the stimulus to impose regimes that rely on their ideological colors, Red you are, Red you will be marginalized and do not cross the line drawn in the sand. Against this, we have “Pueblo Unido Jamas Sera Vencido” and “No Passaram”.
Populism, the defense of Western and Christian values , and socio-fascism became the new popular formula fueled by the masses by the regimes that collaborated with the new form of multinationalization of capital and circulation of money.
The avalanche of credits and loans distributed like “time bombs” in Latin America and Africa by vile bankers wanting to get rid of the excess dollars circulating in the world and this at all costs and with damning conditionalities and exorbitant interest rates bordering on catastrophe for creditor countries (the new financial imperialism allies itself with neo-colonialism to give birth to subcapitalist structures around central Euro-American capitalism) and this with the help of the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (the spoilsport twins emerging from the Bretton Woods agreements). This is what has happened since then, there is no talk of the evolution of monetary policies advocated by Europe – EEC, EC, EU and ECB, Reserve Federal Bank, and the USA,
Dizzying inflation, stagflation, external deficits, depression, and recession combined with the brokerage and corruption of Technocrats, Bureaucrats, and their military allies took power and reduced to nothing all demands for liberation and national development based on the use of local, regional and national resources. In the part of the world outside the Soviet sphere of control, communist ideology and the policy of “containment” serve as an excuse for the elimination of all social democratic and worker representation as part of a militarization of regimes. in the countries of the South, the surge of Multinationals and the takeover and monopoly of international distribution circuits and division of labor as well as manufactured products with higher added value. Forced immigration becomes the means of drawing human resources from countries subject to such practices of dispossession and exhaustion of local natural resources.
The Middle East is becoming the scene of international confrontations just to dominate oil exploitation and its international distribution. The seasons become popular pseudo-revolutions manipulated from the outside with even armies of mercenaries converted to a new Islamist religion that had no reason to exist other than to frighten the rest of the world and present Islam as the continual threat older than fallen communism since it dates from before the Middle Ages, the Modern Crusades are of the moment and serve as a catapult of all Western military interventions in Afghanistan, Iraq, Libya, Somalia, Syria coupled with military base installations not only in the south of all Muslim countries in Africa, the Middle East, Central Asia and even at the gates of Russia.
These military movements had also imposed with them the expansion of Western financial circuits given that the control of natural resources and the denomination of corresponding transactions and military and civil orders are all formulated in Dollars and Euros through banks, and financial centers including Swift which are centered and installed as well as controlled by occult Western financial powers with the help and support if not the guarantees of the Western chancelleries of the European States forming the central framework of the financial decision of the whole European Union, the United States of America and through private and public central banks including the World Bank, IMF, OPIC and their regionalized agencies. To cite just one example,
Saddam Hussein was hanged and Gaddafi was executed not because they were dictators and reproductions of Hitler, but only because they wanted to distance themselves from the Murderous Dollar set up by these multinational banks who want to keep transfers under their domes international deposits and international gold deposits, while all they do is print and serve paper in exchange. If the West was truly in pursuit of the elimination of despots and dictators, we can go back to Franco, Salazar, and down to the Shah, the Presidents of South Africa, Rhodesia, the Philippines, Indonesia, Central and South America, and all these regimes which have committed genocides in North Africa, Sub-Saharan Africa, Asia and even North America.
The sidelining of leaders in Latin America was started by Alberto Fujimori and Ignacio Da Silva Lula who had the misfortune to become president after a civilian interim that succeeded the Military Regime installed by Castello Branco in 1964 and which lasted until the eve of the mid-seventies with the appointment and approval of the military of their civilian allies in the persons of Tancredo Neves and Jose Sarney.
He became president of the Federal Republic of Brazil after president-elect Tancredo Neves fell ill (he underwent emergency surgery on March 14, 1985, hours before his planned inauguration, but did not die until April 1985 from complications of his disease). Originally, Sarney was to be the vice president of the Republic, which was returning to democracy for the first time since 1964 which was the beginning of military rule. To avoid a vacancy in the presidential office, provided for by the Constitution, Sarney took the oath of office on March 15, 1985, with the aim of ensuring what was then thought to be an interim period of approximately one week. The death of Neves will decide otherwise. Brazil’s three main problems are urban poverty, high inflation, and a huge foreign debt.
To fight against the hyperinflation affecting the country, José Sarney decided to implement a heterodox economic plan, like other Latin American leaders, such as Raúl Alfonsín in Argentina (1983-1989) or Alan García in Peru (1985-1990), wishing to embody an alternative to the recommendations of international financial organizations, such as the IMF, which advocate the adoption of neoliberal economic policies. The Sarney plan includes, among other things, the freezing of prices, the adoption of the cruzado, which replaces the cruzeiro (1 cruzado = 1000 cruzeiros), and the freezing of the exchange rates of the new currency. Initially, the plan succeeded in containing inflation, but it started again very quickly because the structural causes of hyperinflation were not combated. Sarney’s successors, starting with Fernando Collor de Mello, will follow neoliberal policies in accordance with the recommendations of international financial organizations.
Mexican Foreign Minister Marcelo Ebrard announced Wednesday that the Pacific Alliance summit, scheduled for December 14 in Peru, has been suspended due to the motion of censure voted against its president Pedro Castillo.

“Given the latest events in Peru, it was agreed to postpone the Pacific Alliance summit which was to take place on December 14 in the city of Lima. I will keep you informed,” he said on his official Twitter profile.
Ebrard also stressed in another message on the same social network that “Mexico regrets the latest events in Peru”. “He hopes for respect for democracy and human rights for the good of this dear brother people,” he added.
The meeting of leaders of the group, which is made up of Colombia, Chile, Mexico, and Peru, was scheduled to be held November 24-25 in Mexico but was suspended because Castillo could not leave Peru as part of the investigation against him for corruption.
Mexico was to cede the pro tempore presidency it has held since 2018 and Costa Rica, Ecuador, and Honduras were to join the group, founded in 2011.
Peru’s Congress voted to remove President Pedro Castillo from office this Wednesday, December 7, 2022, and replace him with Vice President, Dina Boluarte, shortly after Castillo attempted to dissolve the legislature ahead of a planned vote to impeach him. The national ombudsman’s office called Castillo’s attempt to dissolve Congress a coup.
Lawmakers then voted 101-6 with 10 abstentions to remove Castillo from office on grounds of “permanent moral incapacity.” Shortly before the vote, Castillo announced he was installing a new emergency government and called on the next round of lawmakers to craft a new constitution. He said in a televised address that he would govern by decree in the meantime, and ordered a nighttime curfew starting Wednesday evening.
Castillo also announced he would make changes to the leadership of the judiciary, the police and the constitutional court. The head of the Peruvian army then resigned, as did four ministers, including those of foreign affairs and the economy.
Castillo took the action as his opponents in Congress moved toward a third attempt to impeach him.
The Office of the Ombudsman, an autonomous government institution, said in a statement before the congressional vote that after years of democracy, Peru is in the midst of a constitutional collapse “that can only be described as a sudden collapse. ‘State”.
The office called on Castillo to resign and surrender to judicial authorities.
“Mr. Castillo must remember that he was not only elected president of the Republic but also that the people elected representatives for public service,” the statement said. “Castillo’s actions ignore the people’s will and are invalid.”
The congressional vote called for Vice President Dina Boluarte to assume the presidency. Boluarte via Twitter rejected Castillo’s actions, saying that “this aggravates the political and institutional crisis that Peruvian society will have to overcome in strict compliance with the law.”
Changes of Presidents in Latin America and Africa are reactions to external pressure and the impact of sudden changes of allegiance and the direction of the international situation, especially in the countries of the North and Western economies.
2022 December 25

by Said El Mansour Cherkaoui
THE NEW VERSION OF THE THEATER PLAY LES MISERABLES FACED INFLATION IN CALIFORNIA

They were waiting for the European storm to pass over the global economy and they held interest rates until the Fed and Mrs. Lagarde decided that it was no longer possible to have and be in the position to wait and see or wait for Godot.
Unfortunately, the Fed’s first increase was a response to financial obstruction of the British economy. Still, it was met with OPEC’s decision to cut oil production, Russia’s decision to only accept rubble as a means of payment, and the decision of the Chinese to make payment only with the Yuan for all external transactions. The conglomeration of all these geo-economic actions caused the dollar to be the first higher than the euro on the international market while it also increased its vulnerability to emerging markets as it impacted more than 60% of indebted countries that are on the verge of default with Zambia, Sri Lanka, and Ghana at the forefront of full default.
In November 2020, Zambia made headlines when it became the first African country to default on its debt to foreign lenders during the COVID-19 global health crisis. While many African countries made significant progress in reducing their debt burdens in the 1990s and 2000s, in recent years countries such as Zambia, Kenya, and Mozambique have steadily taken out more and more loans to finance major infrastructure projects and public spending. In 2021, Zambia’s overall debt burden reached 123% of the country’s GDP according to the International Monetary Fund. Such a public debt burden poses a threat to long-term economic stability and impacts the delivery of services to citizens,
The recession was no longer at the periphery of Western economies, it was spreading beyond the surge in inflation of energy, raw materials, and the accessibility of basic foodstuffs by many countries.
Also, Japan has always played the role of antechamber and echo chamber for the American economy since the Reaganomics and Economic School of the Chicago Boys.
Inflation that was stored like a volcano once the solid ground of all decisions made by financial and government agencies on the Western side of history, continued liberalism has erupted in flames and lava covering the rest of the world economy and the price of energy produced combined with the disruptive nature of all diseases have smoothed the way for stagflation to take up residence in the best of the best financial and economic houses that is the value of manufactured products, the value added to primary goods by the international division of technological and logistical labor and the continual decline in the value of commodities and primary goods from the south.
The subsequent division between nations has the same line that divided the Town-Dwellers and financiers and the peasant serfs sold the land as part of the value of the land which depreciated in view of the interest charged by the Burgher-bankers to landowners. far remained cloistered in what was called the Faux-Bourg, Faubourg on the outskirts of the Center, that is to say, the Market Square of the City where monetary circulation is the main framework for commercial transactions while the Faubourg more is about barter as a method of exchange which adds more dependence to the Central Merchant Market, these are the classes which were the first investors in the next industrialization of the Bourg, first through the artisans and corporations before further separating themselves from the skills and abilities of the staff and becoming the property of the productive mechanisms which made them become the extension of massive mechanical production. a system that takes individual initiative or collaborative craft team.
Such a separation and the abuses that resulted from it made it accepted by this new class of workers who at this period of time had only one thing but their Clog – Country Wooden Shoe / Sabot – to stop this crushing of their appropriation of theirs. labor or the product they produce. They had to throw their wooden clogs/sabots into the machine so they could take a break. A strategy that gave us the name Sabotage was the age of Sabot in reverse of the means and methods of production.
Diseases and the reduction in agricultural production added to the continual rural exodus have made the condition of the people who rely only on the strength of their arms and hands to beg for bread:
TELL THEM NOT TO THROW AWAY THE CRUST OF THE CAKE SO THEY WON’T BE HUNGRY ANYMORE
– Marie-Antoinette’s sentence distorted over time.
A long time ago, in the USA and the West where we began to specialize in the Daily Production of JEAN VALJEAN ET LES MISERABLES by our Great Victor Hugo, it was the era of “Huguenots = Huge money but you got not” in the USA.
In the United States, California, we are manufacturing a new food market robot and it is called:
A new superhero named Jean Valjean resulted from inflation and especially the price of bread as it was in the time of the miserable
The Ciabatta Bread – Baguette – Batard named Bastar is priced between 5 dollars to 8 dollars, and guess what…
Basically, the price of 35 dozen eggs is over $100, which means one egg costs $2.8571.
We invoke Hashem God and Allah when we are in difficulty, I mean apart from the troubles that despite having flour, water salt, and a hot oven, we cannot make dough and we lack wheat, Ukraine the Granary of the liberal Western Empire and Africa, as used to be North Africa – called Mauretania the Granary of the Roman Empire.
The shortage of wheat has caused so many changes of government and empire and with Ukraine, it loses the transfer of wheat to the rest of the world and with this wheat, it impacts the circulation of money and the use of the dollar for these products. So, well my brother, we have not yet come out of the mill and we are cooked before grinding the dough into disorder despite everything we have taken from Hashem, God, and Allah, and this time in contradiction to our own wishes, putting ourselves in difficulty to make bread, what new pain to wish yourself to be swallowed up in troubles and all this to resupply yourself and monetize it with wheat, with money for tomorrow, today, while waiting for Godot and being in difficulty, we eat dry bread, French toast without eggs, and as they say,
Since you can’t be a baker or like the former French Prime Minister who got into trouble with all of France or like a baker who makes balls in a bread mixer, then you can always try to be a cook
Also, as they say: if you can’t stand the heat, get out of the kitchen and let the Palos make their own bread without dirtying or burning their ovens.
Hasta la Vista Hermano and Bon Appétit. It’s not just boiling but burning inflation
In Africa, we are stocking up on Aces and we are going to starve our people to serve and feed their Gargantuan Growing Appetite which has no limits
African states feed the debtor and starve for his own appetite
in the productive, operational, and logistics infrastructure and in the upstream supply chain of raw and peripheral materials and packaging at all stages of the transfer and exchange of goods and intermediate products from source to distribution and to the direct and indirect sale of the final product.
17/12/2022
Regarding FTX and the Madoff analogy, here’s another one:
In 2008, #hedgefund accountants turned a blind eye to the questionable valuations of private assets. There was a whole category of funds that showed great results with virtually no volatility – return smoothing at its finest. A #hedgefund specializing in, for example, private loans could say: “Hey, the accountants approved it”.
Madoff was a wake-up call – in December 2008, accountants realized they could be held liable for erroneous net asset values. So they turned the screw and soon some hedge funds were forced to write down assets held at invented values.
Clearly, the accounting profession as a whole has kept its distance from #crytpo, perhaps based on what they learned at the time. But the article below in Bloomberg suggests that any company active in the space will be in a mad rush to understand whether the teams focused on this area have followed reasonable professional standards or, as we keep hearing, have been hit and compromised. Those who find problems will prepare cases to help regulators try to limit reputational and financial damage.
“The United States is spending an extra fraction of its defense budget to pay for American industry, which in turn arms Ukraine as it dismantles the Russian threat to Europe.” Kurt Volker.
Said El Mansour Cherkaoui – Oct 3, 2022
Christine Lagarde President of the European Central Bank 53 articles Following May 23, 2023, On 1 June 1998, the European Central Bank was established to prepare for the launch of the euro – the world’s largest ever currency changeover. As a lawyer at the time, I remember how frantically we were revising contracts based on foreign … Continue reading
Said El Mansour Cherkaoui – Global Public Relations Manager at Tate Yoko Research Institute – TRIGlobal Public Relations Manager at Tate Yoko Research Institute – TRI One of the results of Operation Kamikaze taken by the European Central Bank President Christine Lagarde who following a consultative meeting with the International Monetary Fund’s President, she insisted that … Continue reading
Mar 20, 2023 Said El Mansour Cherkaoui – Dear Readers and Friends: It is our pleasure to share with you this Dossier – Analytical Study addressing the present challenge of the financial system and the banking sector which we have titled: “Redefining Banking Globalization” Which we present it to you in the form and content as: “ Dossier – Analytical Study on Cranked Globalization, Tossed Financial Capitalism, Derailed Banking System “. Your comments and suggestions are always welcomed. Please feel free to share our publications with your colleagues, acquaintances and family members including your neighbors. Thank you for your support. … Continue reading
“Monetary policy is to orient economic activity by regularizing the money supply” Monetarism, Liberalism and Globalization: US Reactions and Coronavirus Clashes The Aftermath of Coronavirus? Is this a Mathematical Formula or New Readings of Economic State Intervention? Where is the Invisible Hand of the Market? A second reading more sincere of the works of … Continue reading
Tags: Africa , South America , Asia , China , International Finance , Subcapitalism , European Union

Spontaneous response from Said El Mansour Cherkaoui on this subject
The issue addressed by this video and this presentation remains important for the future of the world, not only commercial, economic, political, and financial but above all on relaxation and mutual understanding as well as the common solidarity which can and must exist between people of different regions of this world.
It’s a really poor explanation and really a waste of film and time looking at nonsense.











